Trees
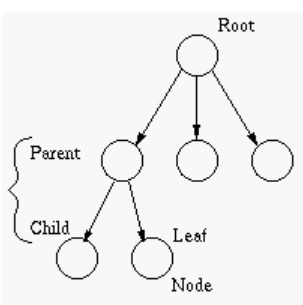
Trees are a hierarchical data structure, each element is a node, you have parent and child nodes, each child has one parent apart from the root node, the child nodes that are not parents are called leaf nodes. You can see an example of a tree structure in the below diagram. I have also covered trees in my Java Reference section. A Binary Search Tree (BST) has 0, 1 or 2 child only, a BST can be complete (leaf nodes are all to the left) or full (all parents have two children), left child is always smaller than its parent and the right child is larger than its parent, this allows for faster searching, height and balance of the tree determines the time complexity which can get O(logn)
| Tree Node | package uk.co.datadisk.tree;
public class TreeNode {
private int data;
private TreeNode leftChild;
private TreeNode rightChild;
public TreeNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public void insert(int value){
if (value == data){
return;
}
if ( value < data){
if(leftChild == null){
leftChild = new TreeNode(value);
}
else {
leftChild.insert(value);
}
} else {
if (rightChild == null){
rightChild = new TreeNode(value);
} else {
rightChild.insert(value);
}
}
}
public void traverseInOrder() {
if(leftChild != null) {
leftChild.traverseInOrder();
}
System.out.print(data + ", ");
if(rightChild != null){
rightChild.traverseInOrder();
}
}
public void traversePreOrder() {
System.out.print(data + ", ");
if(leftChild != null) {
leftChild.traversePreOrder();
}
if(rightChild != null){
rightChild.traversePreOrder();
}
}
public void traversePostOrder() {
if(leftChild != null) {
leftChild.traversePostOrder();
}
if(rightChild != null) {
rightChild.traversePostOrder();
}
System.out.print(data + ", ");
}
public int min() {
if (leftChild == null) {
return data;
} else {
return leftChild.min();
}
}
public int max() {
if (rightChild == null) {
return data;
} else {
return rightChild.max();
}
}
public TreeNode get(int value) {
if (value == data) {
return this;
}
if (value < data) {
if (leftChild != null){
return leftChild.get(value);
}
} else {
if (rightChild != null) {
return rightChild.get(value);
}
}
return null;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public TreeNode getLeftChild() {
return leftChild;
}
public void setLeftChild(TreeNode leftChild) {
this.leftChild = leftChild;
}
public TreeNode getRightChild() {
return rightChild;
}
public void setRightChild(TreeNode rightChild) {
this.rightChild = rightChild;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "data = " + data;
}
} |
| Tree | package uk.co.datadisk.tree;
public class Tree {
private TreeNode root;
public void insert(int value){
if ( root == null){
root = new TreeNode(value);
} else {
root.insert(value);
}
}
public void traverseInOrder() {
if (root != null) {
root.traverseInOrder();
System.out.println();
}
}
public void traversePreOrder() {
if (root != null) {
root.traversePreOrder();
System.out.println();
}
}
public void traversePostOrder() {
if (root != null) {
root.traversePostOrder();
System.out.println();
}
}
public TreeNode get(int value) {
if (root != null) {
return root.get(value);
}
return null;
}
public void delete(int value) {
root = delete(root, value);
}
private TreeNode delete(TreeNode subTreeRoot, int value) {
if( subTreeRoot == null) {
return subTreeRoot;
}
if(value < subTreeRoot.getData()) {
subTreeRoot.setLeftChild(delete(subTreeRoot.getLeftChild(), value));
} else if (value > subTreeRoot.getData()) {
subTreeRoot.setRightChild(delete(subTreeRoot.getRightChild(), value));
} else {
// Cases 1 (left only) and 2 (one child either left or right only): node to delete has 0 or 1 child(ren)
if ( subTreeRoot.getLeftChild() == null) {
return subTreeRoot.getRightChild();
} else if (subTreeRoot.getRightChild() == null) {
return subTreeRoot.getLeftChild();
}
// Case 3: node has two children
// Replace the value in the subTreeRoot node with the smallest value
// from the right subtree
subTreeRoot.setData(subTreeRoot.getRightChild().min());
// Delete the node that has the smallest value in the right subtree
subTreeRoot.setRightChild(delete(subTreeRoot.getRightChild(), subTreeRoot.getData()));
}
return subTreeRoot;
}
public int min() {
if (root == null) {
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
} else {
return root.min();
}
}
public int max() {
if (root == null) {
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
} else {
return root.max();
}
}
} |
| Main Tree | package uk.co.datadisk.tree;
public class BinarySearchTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tree intTree = new Tree();
intTree.insert(25);
intTree.insert(20);
intTree.insert(15);
intTree.insert(27);
intTree.insert(30);
intTree.insert(29);
intTree.insert(26);
intTree.insert(22);
intTree.insert(32);
intTree.insert(17);
System.out.println("Tree created");
System.out.print("IN Order: ");
intTree.traverseInOrder();
System.out.print("PRE Order: ");
intTree.traversePreOrder();
System.out.print("POST Order: ");
intTree.traversePostOrder();
System.out.println(intTree.get(27));
System.out.println(intTree.get(17));
System.out.println(intTree.get(8888));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("MIN value = " + intTree.min());
System.out.println("MAX value = " + intTree.max());
System.out.println();
intTree.delete(15);
intTree.traverseInOrder();
System.out.println();
intTree.delete(17);
intTree.traverseInOrder();
System.out.println();
intTree.delete(25);
intTree.traverseInOrder();
System.out.println();
intTree.delete(8888);
intTree.traverseInOrder();
System.out.println();
}
} |
