Oracle Connectivity
Oracle provides Oracle Net Services which is a suite of components that provides a connectivity solution. Oracle Net Service consist of
Database Service Name
Databases logically appear as services, you identify each database in your system by its service name. The database instance name refers to the SGA and processes that make up the instance, this is commonly referred as the Oracle System Identifier (SID), normally a database is only associated with one instance apart from when using a RAC environment. You can uniquely identify each database by using a global database name which is in the format of database_name.database_domain (sales.us.acme.com).
Connection
You need two pieces of information to connect to a database
Oracle supports a number of protocols TCP, SDP, TCP with secure sockets and named pipes. There are two ways to connect to oracle dedicated or Shared Server, both could be running at the same time on the same server. There are 4 connection types
To connect to a oracle service you would use a connect string
| Connect String | connect scott/tiger@(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=sales)(PORT=1521)) connect scott/tiger@sales |
Listener
Oracle listener only runs on the server and listens for incoming client connections, a utility called lsnrctl is used to manage the listener process. The listeners role is
The listener.ora file contains the listener configuration details, with oracle 10g the listener can automatically register itself with the database, The PMON process updates the listener.ora file with any new databases.
| Dynamically register the default listener | 1. Register the default listener to the instance Note: port 1521 is assumed, you do not need to update the listener.ora file |
| Dynamically register a non-default listener | 1. Create the listener (use Net Manager) # alter system set local_listener = 'P01_1522'; Note: you need to update the listener.ora and tnsnames.ora files |
The listener utility lsnrctl can be used to manage the listener
| starting | lsnrctl start |
| stopping | lsnrctl stop |
| status | lsnrctl status |
| Reloading configuration | lsnrctl reload |
| Display Services | lsnrctl services |
| Save the configuration | lsnrctl save_config |
| Set tracing ON | lsnrctl trace |
| Help | lsnrctl help |
| Number of set/show commands | current_listener |
An example listener.ora file
| listener.ora | # listener.ora Network Configuration File: C:\oracle\product\10.2.0\db_1\NETWORK\ADMIN\listener.ora # Generated by Oracle configuration tools. SID_LIST_LISTENER = LISTENER = |
Naming and Connectivity
Oracle also several types of naming services
| Host Naming | c:\> set ORACLE_SID=P01 c:\> sqlplus vallep/secret@laptop Note: DNS will resolve the laptop name |
| Easy Connect | c:\> sqlplus vallep/secret@laptop:1522/P01 c:\> sqlplus vallep/secret@//laptop/P01 |
| Local Naming | Add an entry in the tnsnames.ora file P01 = Note:can use the TNS_ADMIN environment variable to point to different tnsnames.ora files |
The sqlnet.ora file specifies which order to try (bit like the nsswitch.conf file in unix)
| sqlnet.ora | NAMES.DIRECTORY_PATH=(TNSNAMES,EZCONNECT,HOSTNAME) |
File locations
| adaptors | $oracle_home/bin/adapters |
| listener | $oracle_home/network/admin/listener.ora |
| tnsnames | $oracle_home/network/admin/tnsnames.ora |
| sqlnet | $oracle_home/network/admin/sqlnet.ora |
| listener log | $oracle_home/network/log.listener.log |
| server tracing | $oracle_home/network/trace/listener.trc |
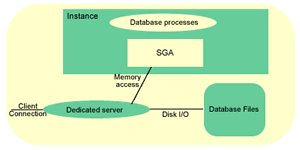
Dedicated Connection
Oracle will create a new process when you log on, this is commonly know as the dedicated server process, the process will exists as long as the connection exists. For every session a new dedicated server process will be created. This process will receive SQL and execute it, read data files and look in the database cache for data. It will also perform update statements and run any PL/SQL code. The flow of this process is seen below:

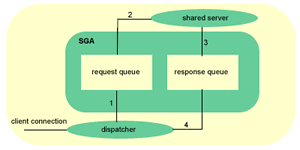
Shared Server Connection
The big difference between dedicated and shared server is that the client process never talks directly to the shared server process. Oracle employs a process called dispatcher which will put clients requests into a request queue in the SGA (1), the first shared server process that is not busy will pick up the request and process it (2), upon completion the shared server will place the response in the response queue (3). The dispatcher process is monitoring this queue and upon seeing a result, will transmit it to the client (4), the flow of this action is seen below:
Normally one shared server process should be able to handle between 10-20 users. A dispatcher should be able to handle about 100 shared server processes. A good rule to thumb when setting the parameter values (pfile or spfile) should be the following:
SHARED_SERVERS should be set for slightly greater than the expected number of shared servers that will be needed when the database is at an average load.
MAX_SHARED_SERVERS should be set for slightly greater than the expected number of shared servers that will be needed when the database is at an peak load
Add dispatcher processes while Oracle is running with the SET option of the ALTER SYSTEM statement to increase the value for the DISPATCHERS initialization parameter.
The total number of dispatcher processes is limited by the value of the initialization parameter MAX_DISPATCHERS. You might need to increase this value before adding dispatcher processes. The default value of this parameter is five, and the maximum value varies depending on your operating system
The big picture
The following diagram details what we have seen before, connection via shared server and dedicated server. It also shows that an Oracle instance may use both connections type simultaneously:
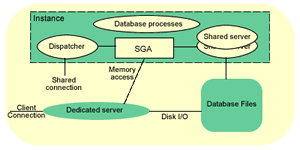
A circuit is a piece of shared memory that the client connections are bound to during communications it is called a virtual circuit.
The background process PMON notifies the listener as to which dispatcher is responsible for servicing each virtual circuit. This information is supplied when you run "lsnrctl services" and has 4 values established, refused, current and max.
Connectivity Setup |
|
| Setup Dispatchers | # alter system set dispatchers="(protocol=TCP)(dispatchers=2)"; # alter system set max_dispatchers = 10; pool - provides connection pooling |
| Shared Server | # alter system set shared_servers = 5; shared_servers - the system will initially start this many (default = 1) Note: If at anytime you get ORA-00018 errors (Logging in or EM reports this error) this is because "shared_server_sessions" has been set too low |
| Circuits | # alter system set circuits = 300; |
Useful Views |
|
| V$DISPATCHER | displays information about the dispatcher processes |
| V$DISPATCHER_CONFIG | displays information about the dispatcher configurations and their attributes |
| V$DISPATCHER_RATE | displays rate statistics for a number of activities performed by the dispatcher processes |
| V$QUEUE | contains information on the shared server message queues |
| V$SHARED_SERVER | contains information on the shared server processes |
| V$SHARED_SERVER_MONITOR | contains information for tuning the shared server |
| V$CIRCUIT | contains information about virtual circuits, which are user connections to the database through dispatchers and servers |
| V$SESSION | lists session information for each current session |
Useful SQL Code |
|
| List the dedicated server processes | select a.spid dedicated_server, b.process clientpid Note: remove the last line for all dedicated processes |
| List the dispatchers | Select * from v$dispatcher; |
| List the shared server processes | select count(*) "Shared Server processes" |
| Display average wait time per request | SELECT DECODE(TOTALQ, 0, 'No Requests',WAIT/TOTALQ || ' HUNDREDTHS OF SECONDS') "AVERAGE WAIT TIME PER REQUESTS" FROM V$QUEUE WHERE TYPE = 'COMMON'; |
| Display levels and maximum levels | select 'session count from v$session', count(*) |
Best Practices
When using shared server make sure that transactions are short in duration, they can be frequent but short, otherwise it will appear to be a total system slowdown due to the shared resources being monopolized by a few processes. So shared server is highly appropriate for an OLTP system (short, frequent transactions). Do not used shared server for data warehousing.
So shared server does 3 things for us: