The Java API documentation is used to create documentation of Java code into HTML by using the javadoc tool. To start the java documenation in a source file you use /** and */ which are picked up by the javadoc tool, the other normal comments (// and /* */) are ignored.
There are a number of tags specific to java documenation which begin with @, some of which I describe below, see the Java documentation for a complete list.
- @author - used for the authors name, you can have multiple @author's
- {@code text}: - same as <code>{@literal}</code>, text will be rendered in code format
- @deprecated - is used to designate a text as deprecated, meaning that the text will be rendered with a bold warning of "Deprecated."
- @see - adds a "See Also" heading with the text entry to links to the reference
- @param - is used to document comments for methods and constructors or classes
- @exception/@throws - adds a Throws subheading to the documentation with the class-name and description text
- @version/@since - the version number, @since is used to indicate the version with which this class, field, or method was added
- @return - provides a description of a methods return value
- @link - Inserts an in-line link with the visible text label that points to the documentation for the specified package, class, or member name of a referenced class.
Below are some examples taken from the Java code
 |
 |
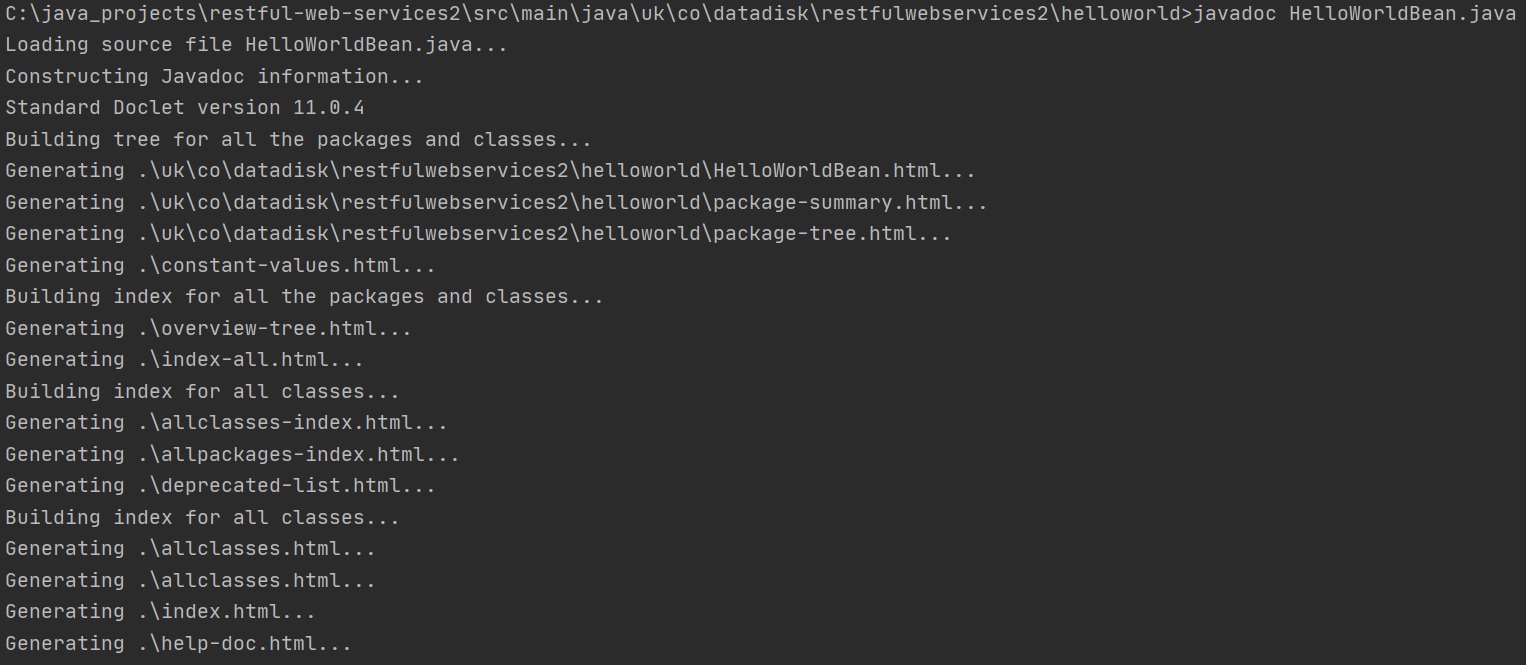
Once you have added the documentation, you use javadoc tool to create the HTML files, as per below, a number of HTML files are created
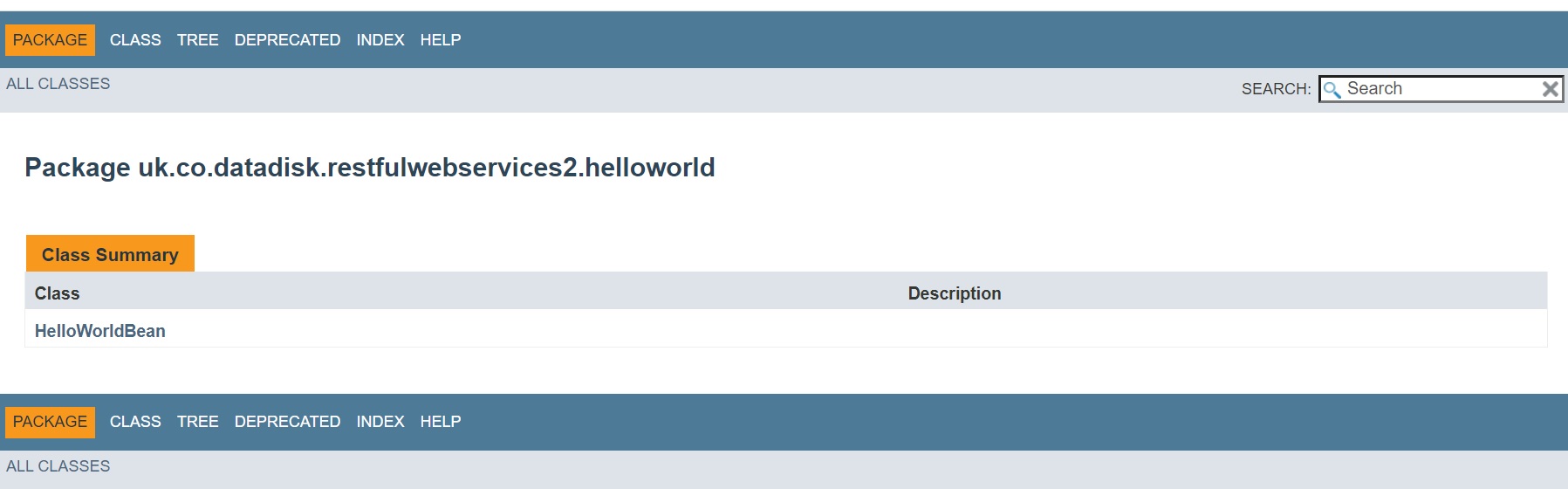
You can view in a standard web browser as per below
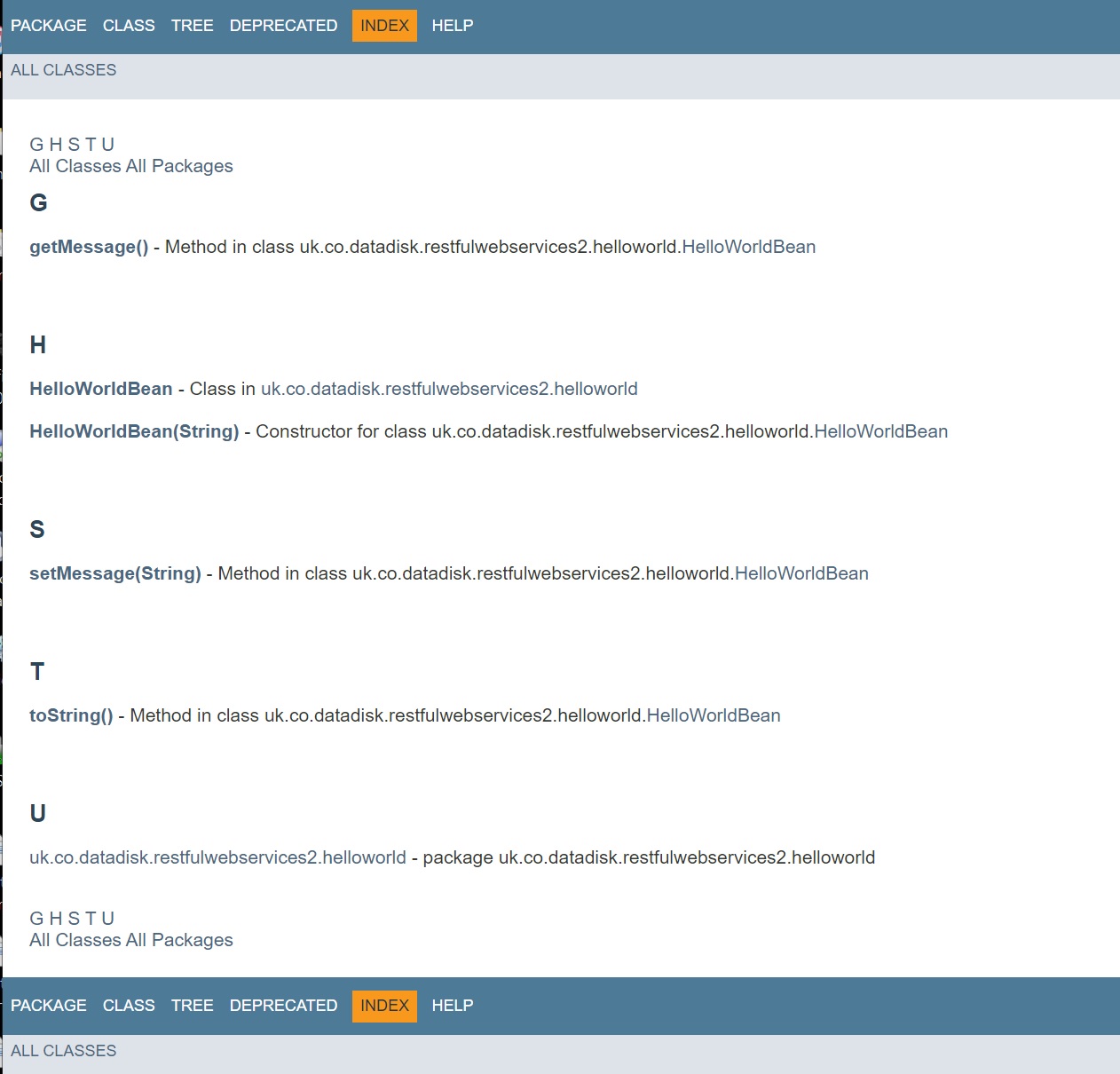
It will create documentation for all the methods, overview tree, etc.
Swagger allows you to document the back-end REST API's for a client, the API documentation should be informative, readable, and easy to follow, doing this manually can be very time consuming. Swagger allows you to Streamline your API’s build process by keeping its design, documentation, and implementation synchronized and updated automatically. I will cover the basics and then leave to explore other features of Swagger. When exposing REST API's the client could be another Java client, PHP client, Python client all these clients should be able to determine how to use the REST API via the documentation you offer them via Swagger. Swagger also offers a UI component that can be accessed via a standard browser, we will see this later.
There are a few dependencies that you need to pull in (left-hand screenshot), you can see what other dependencies are required (right-hand screenshot).
 |
 |
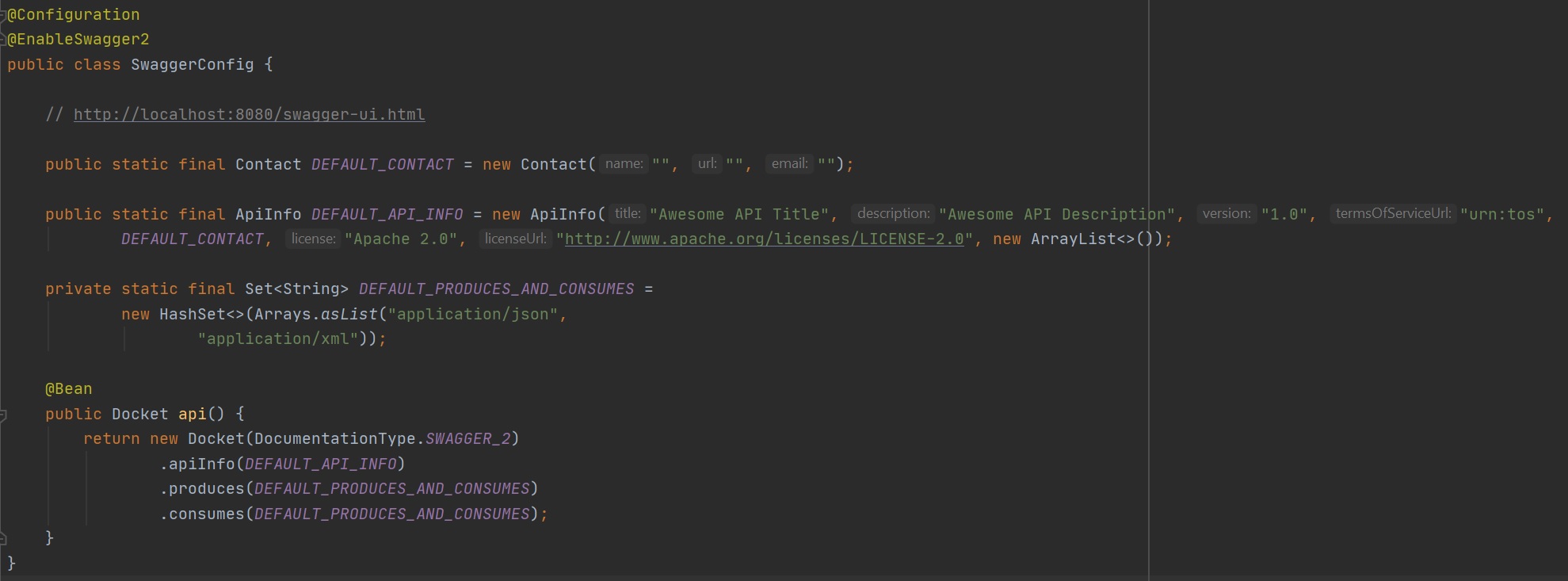
To enable swagger we create a configuration file using @Configuration and use the @EnableSwagger2 annotation, you can then create a Docket which affects the output, I have created default contact, default api info and the default producers and consumers.
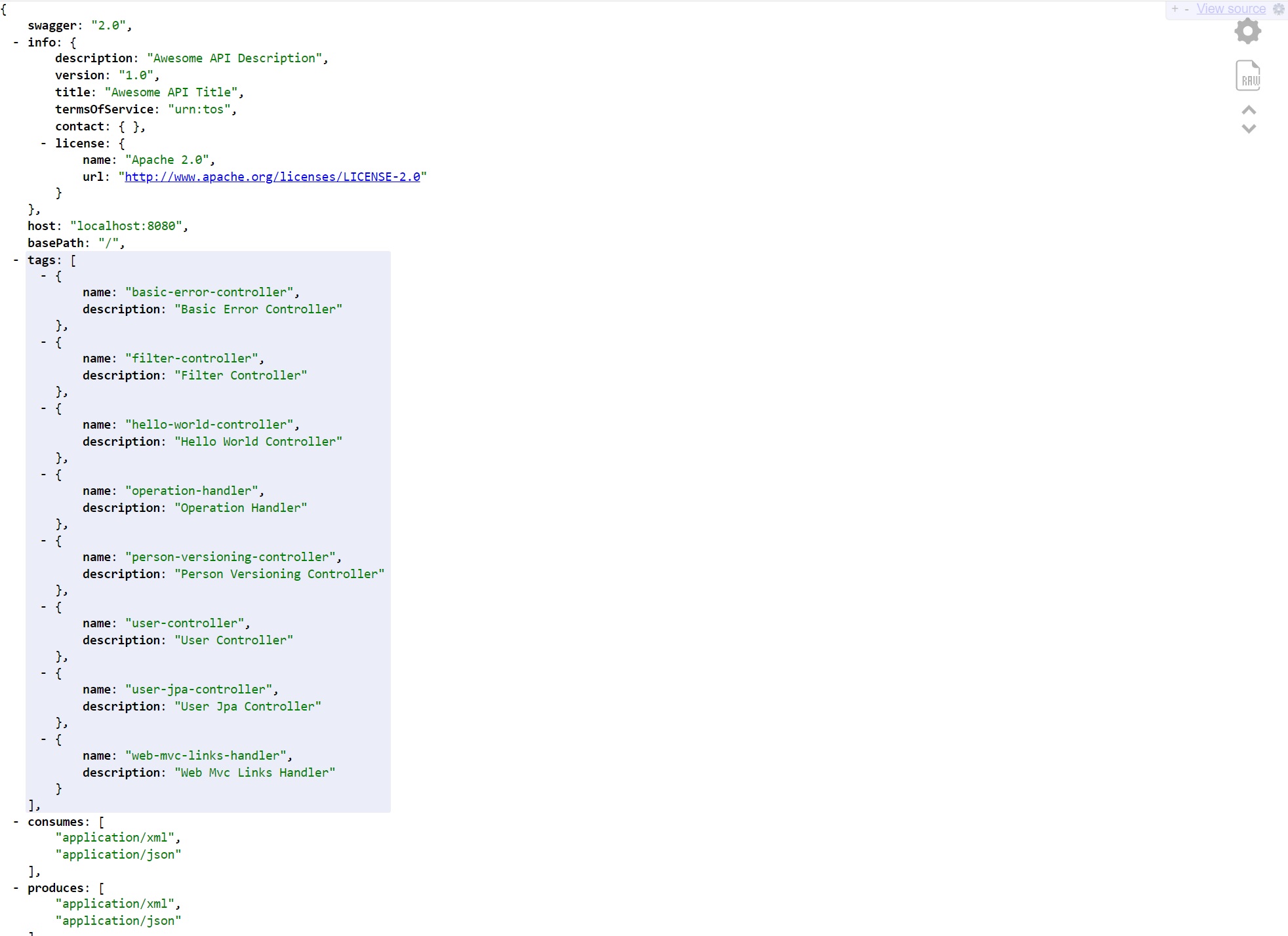
Start the application and using the URL http://localhost:8080/v2/api-docs displays the below, I do have a JSON pretty formatter installed in Chrome, this can then be used by other API clients.
You can now also use the Swagger-UI by using the URL http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html as seen below.
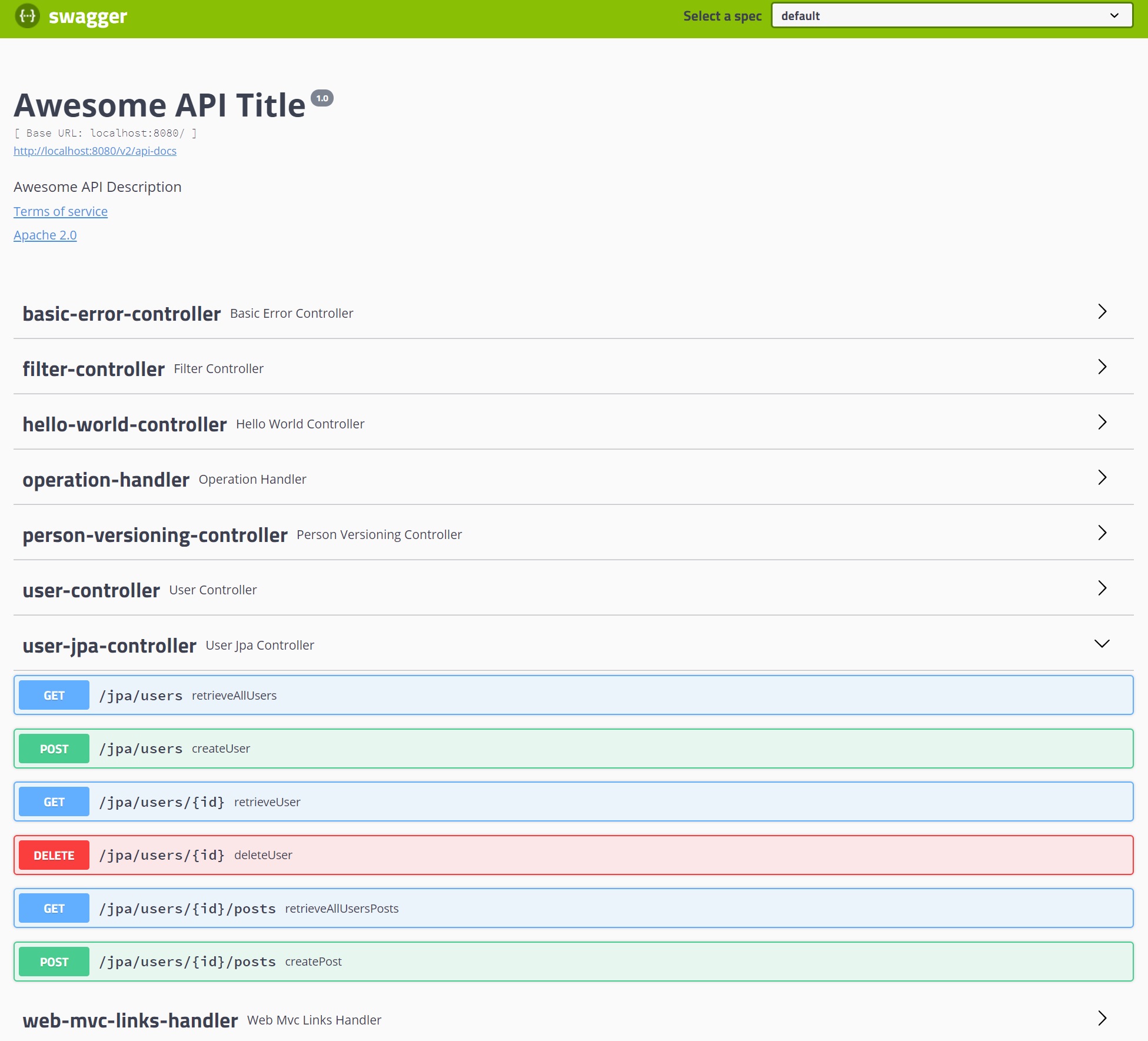
You can even drilldown to each HTTP method, the example is the POST method.
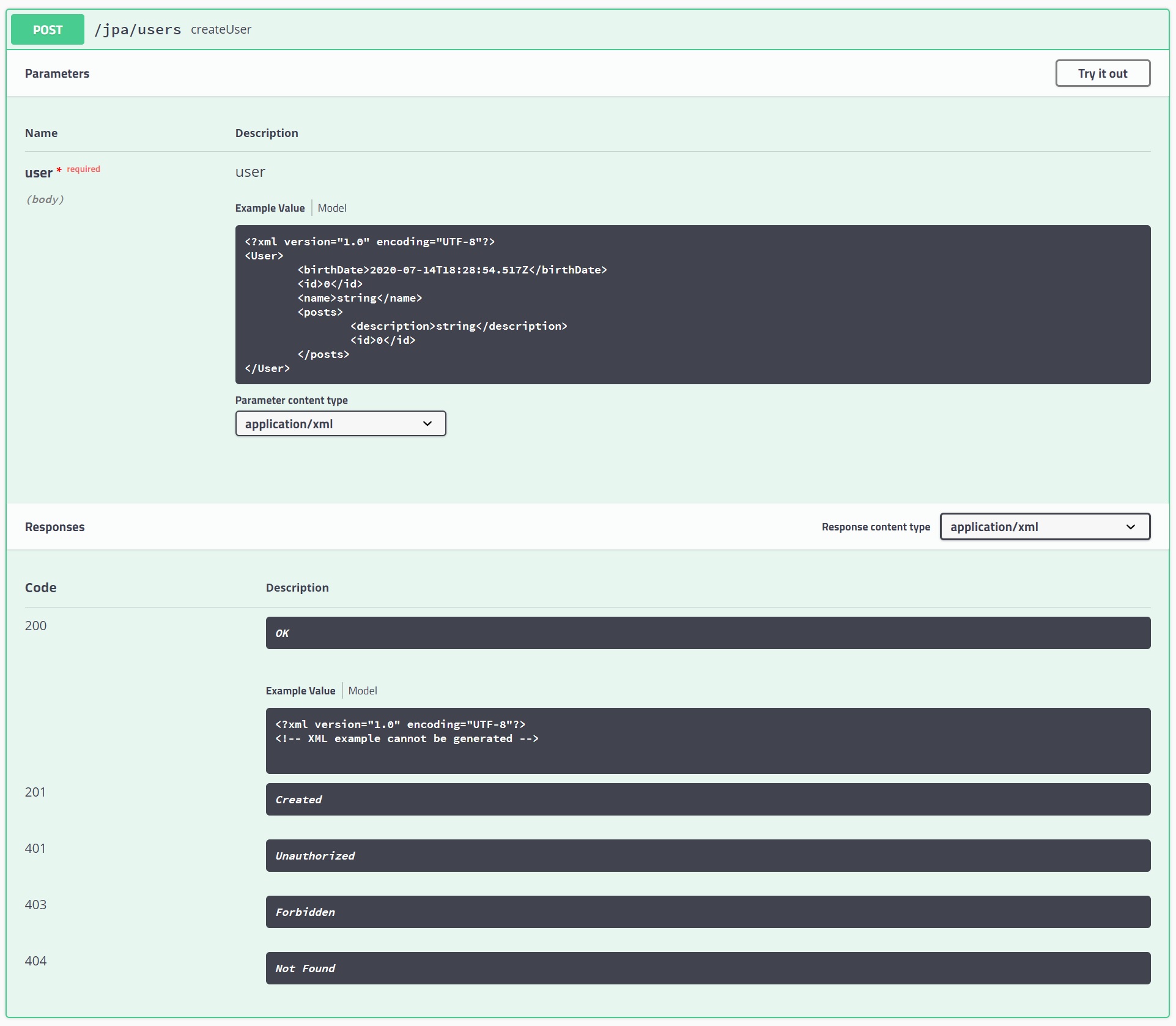
You can even execute commands and retrieve the commands to use
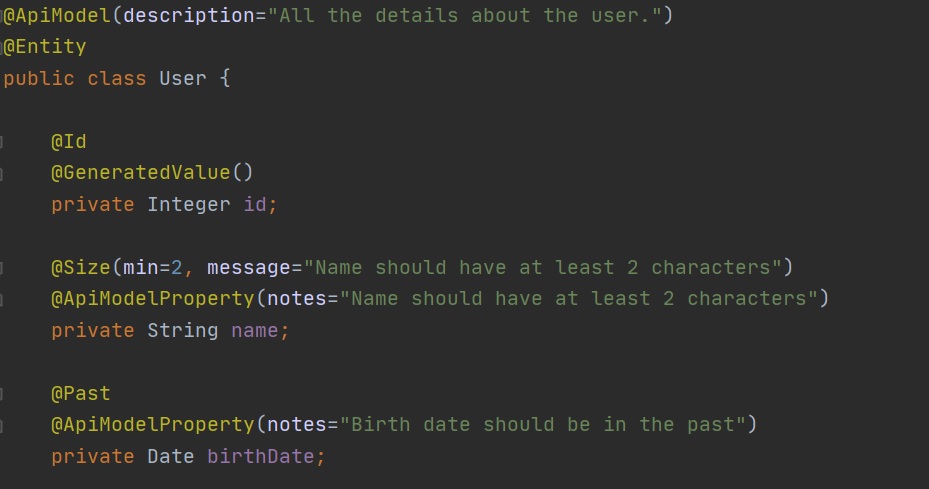
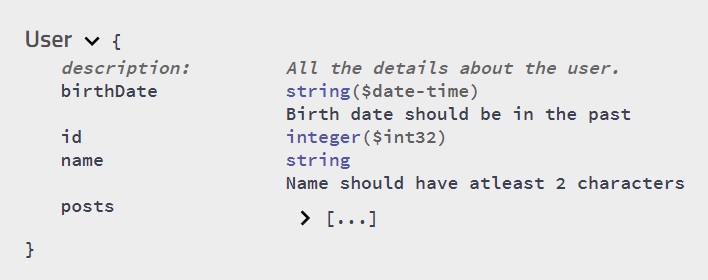
You can provide your own documentation for Model (classes), fields and methods, using either the @ApiModel, @ApiModelProperty, @ApiOperation annotations.
 |
 |
Swagger also has an editor but I will leave you to the Swagger web site for details on how to use this.
Hypermedia as the Engine of Application State (HATEOAS) is a component of the REST application architecture that distinguishes it from other network application architectures, the representations returned for REST resources contain not only data but also links to related resources.
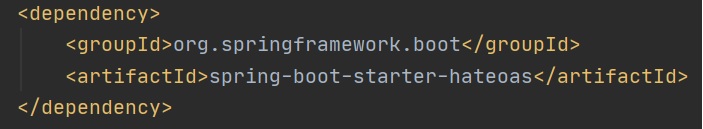
In order to use HATEOAS we need to pull in a dependency as show below
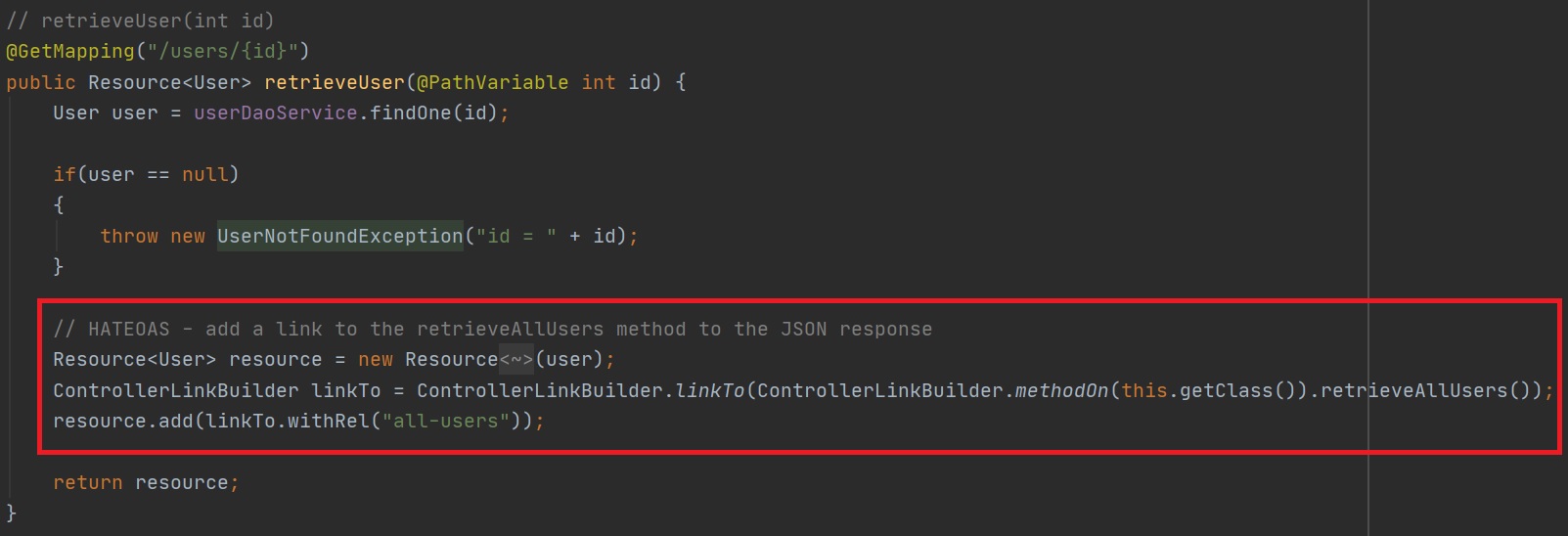
In the below example we configure HATEOAS in a controller method, we start by creating a HATEOAS resource around the user object, next we can add links to the resource, we use the ControllerLinkBuilder to create a link to a method in this case the retrieveAllUsers() method, lastly we when add the link we just created to the resource, we also give the link a name in this case "all-users"
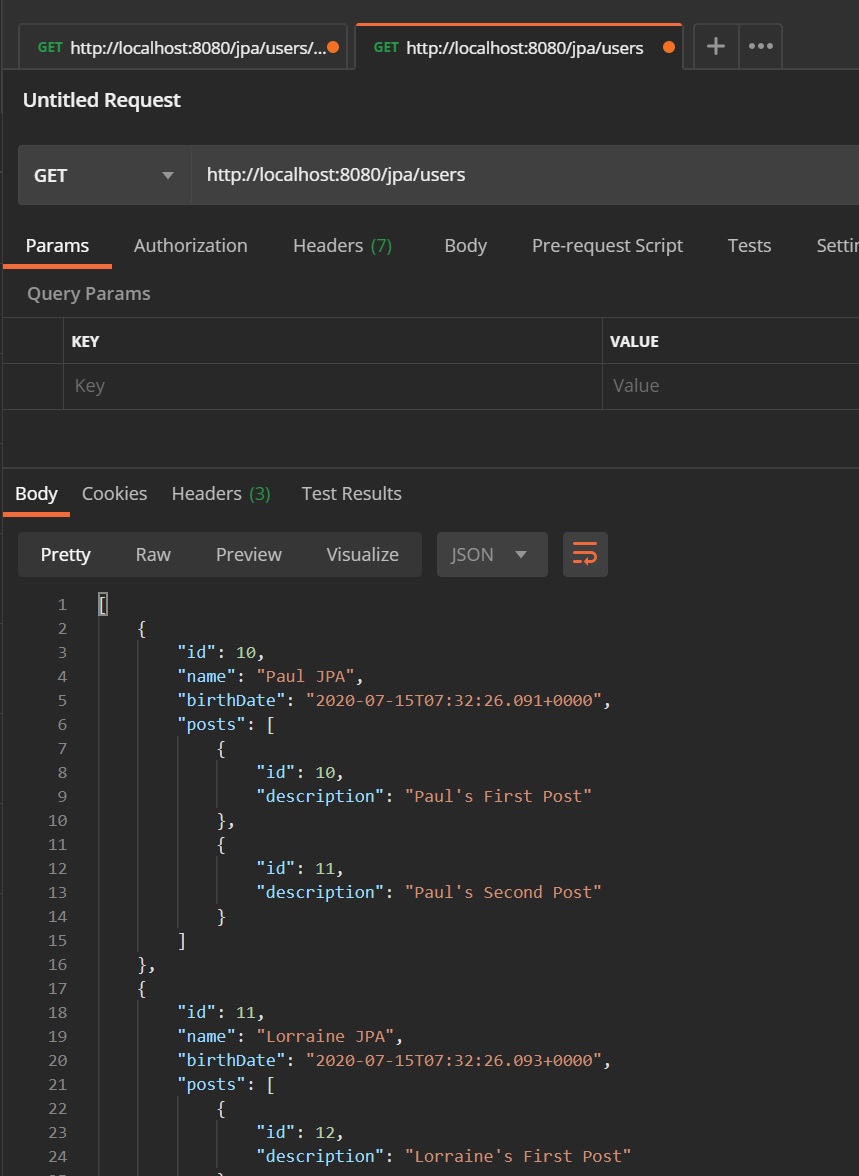
We can then use postman to display the data with the HATEOAS link, as you can see below we have the all-users link pointing to a href that will execute the retrieveAllUsers method in the controller.
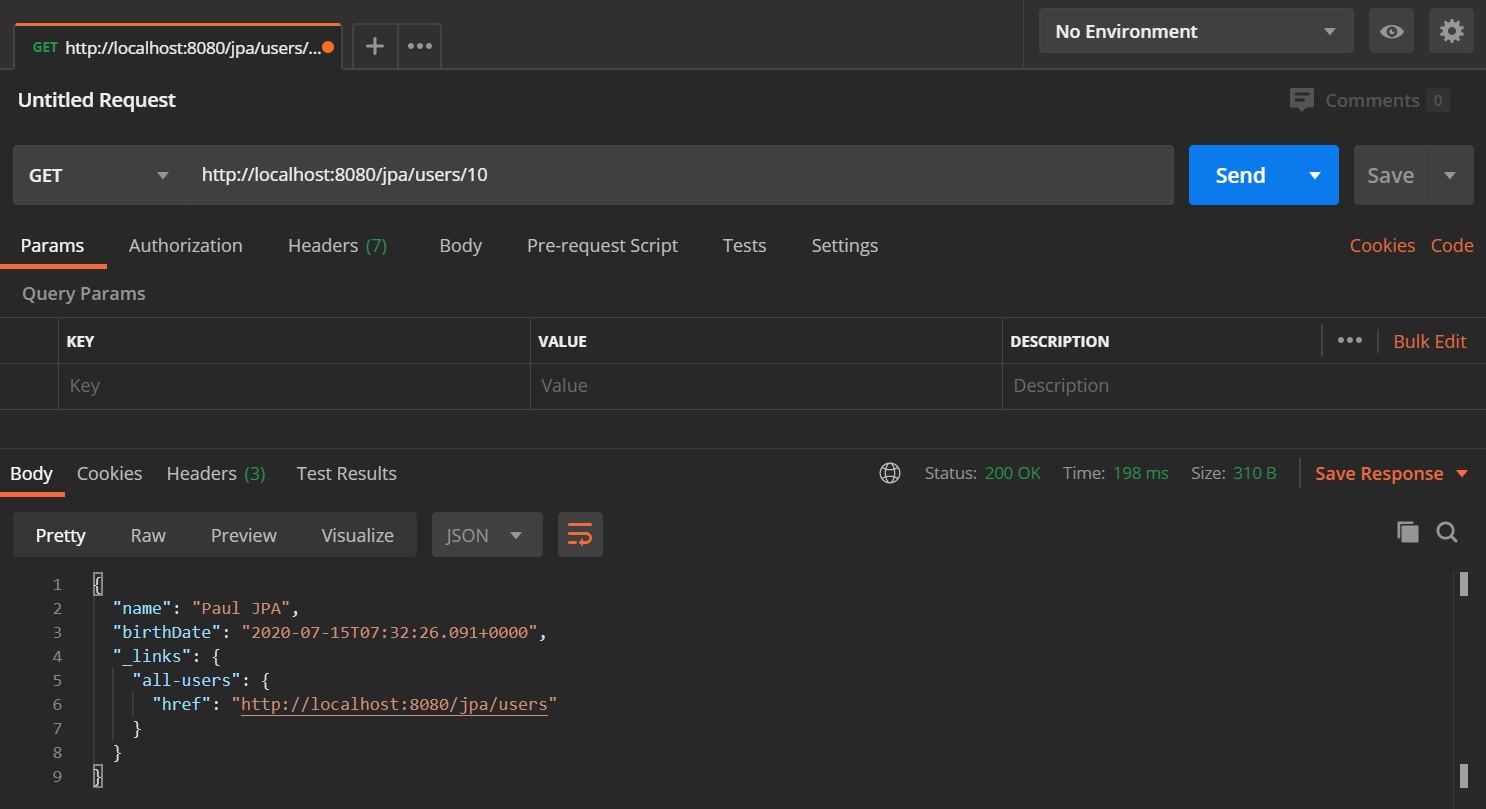
We can then use that link to retrieve all the users as per below