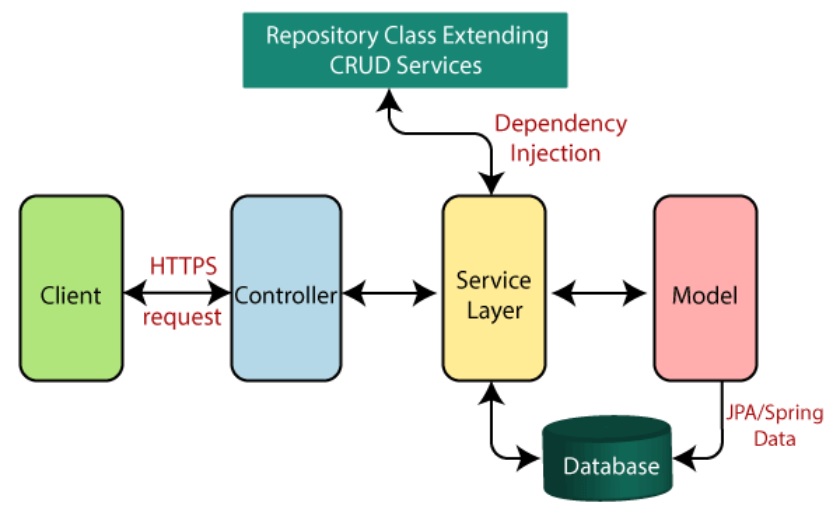
The service layer provides logic that can operate on data that is sent to and from the database, as you can see in the diagram below it sits between the controller and the model layers, as data passes through the service layer you can manipulate the data before sending to the database or back to the controller to the user, the service layer is also known as the business logic layer, business logic should not be performed in either the controller or the model layer. This is a classic MVC setup that has been used for many years now. The service layer uses the Spring repositories for the CRUD operations.
I am not getting into a debate in if you should use interfaces or not, I will leave that for you to decide, I personally have used interfaces which will be reflected in the examples I will be showing below. The first thing to notice is that we annotate the class with the @Service annotation, this means Spring Boot upon startup will load it into the persistence context which makes it available for dependency injection. Next we use dependency injection to bring the classification repository, which will gives the CRUD operations into the database. The form mapper I will discuss in my controller section as this is using MapStruct which simplifies mappings between Java beans also known as Data Transfer Object (DTO).
 |
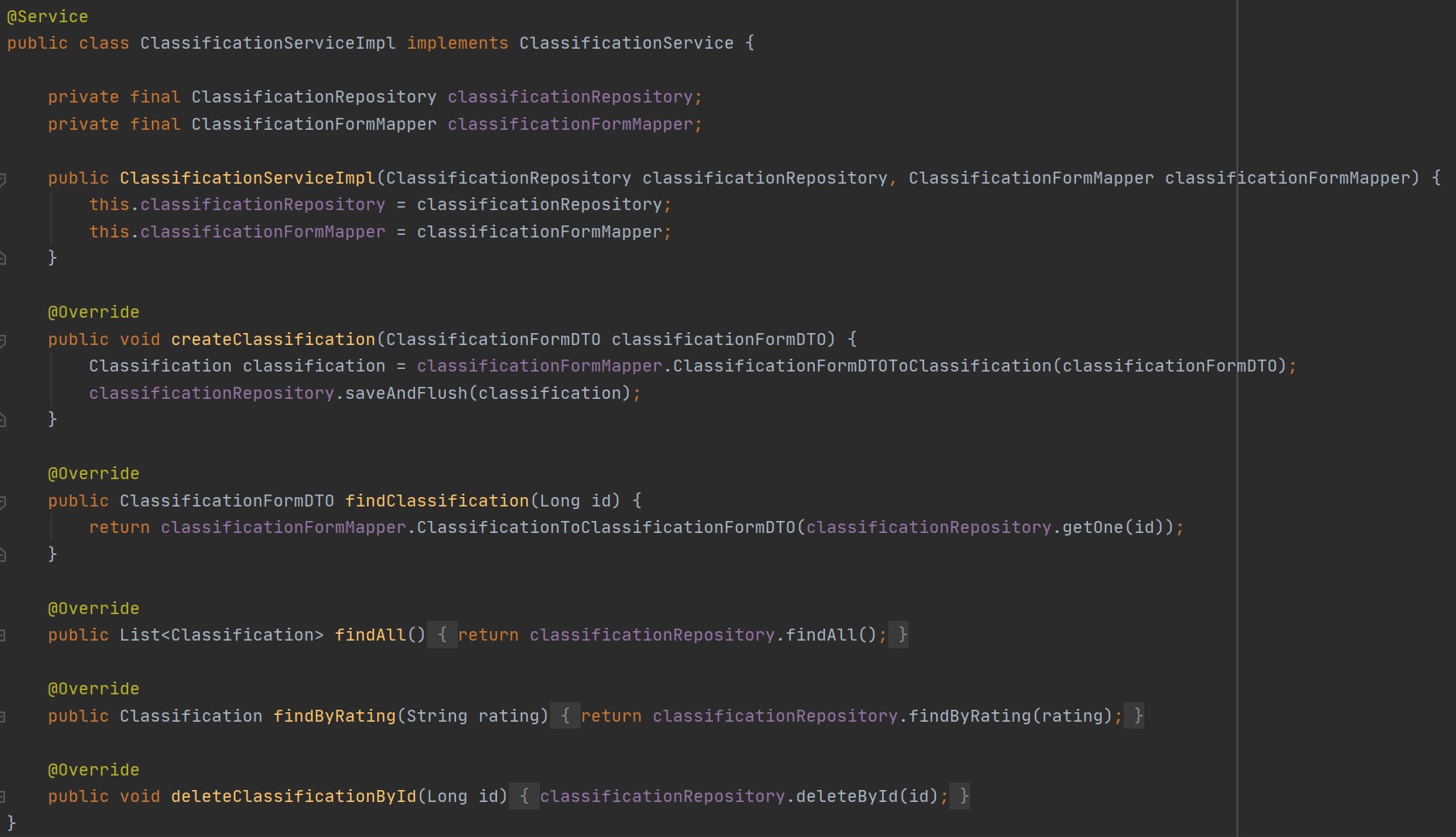 |
Looking at the various methods in the above below screenshot, they all use the classification repository to either create, read, update and delete rows within the database, they use the already provided methods by the JpaRepository as seen below (CrudRepository example show), this makes coding very easy as you are using provided and proven methods that have been tested by Spring. As I am not using much business logic to manipulate the data the methods are very straight forward, also you can use any additional Queries that you have created in the repository as well.

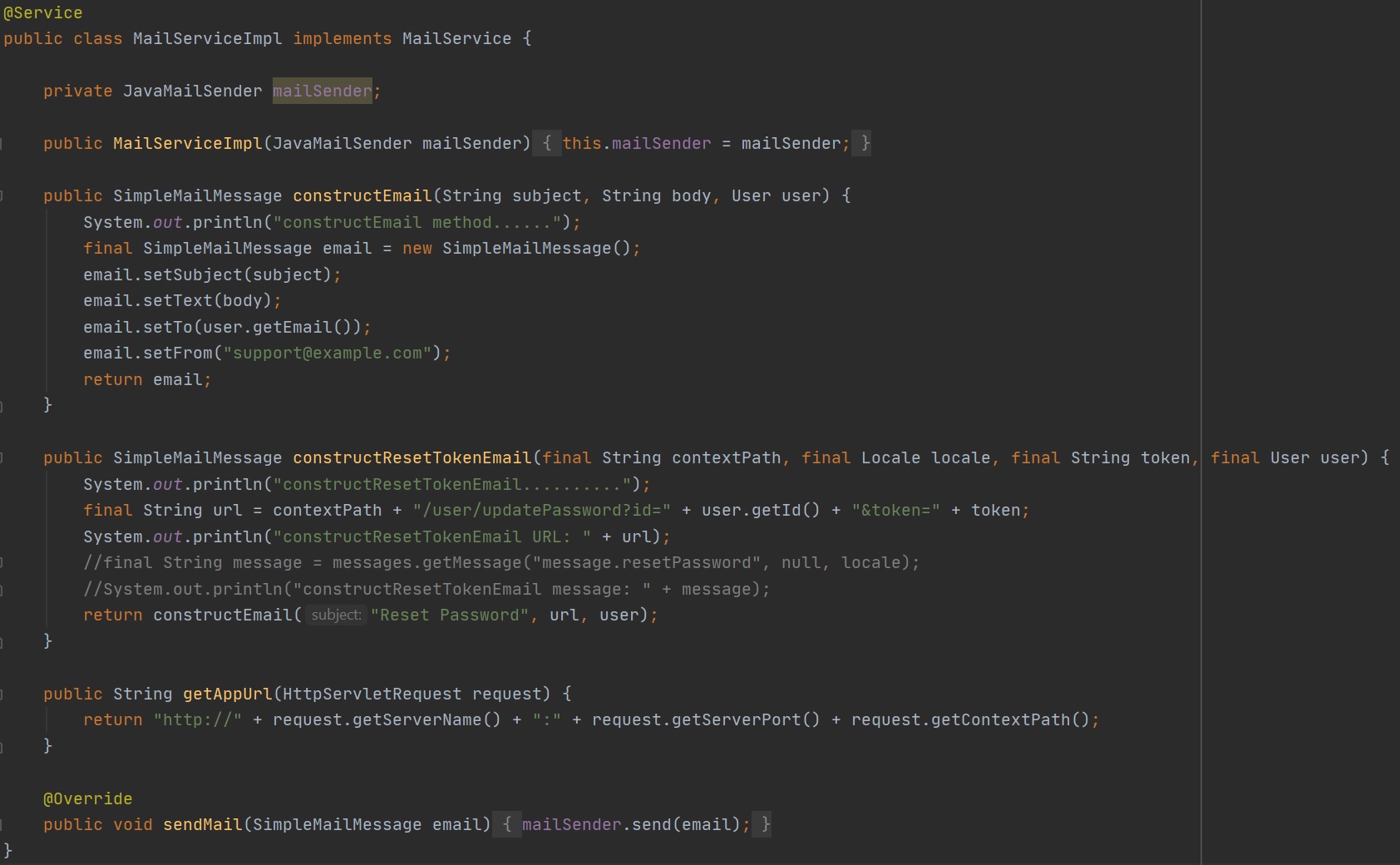
But don't think that the service layer is all about repositories or databases, you can use the service layer to provide any service you like, for example below I have created a email service and this can be injected anywhere and used thats the beauty of dependency injection, you can create services like excel file upload, external financial data retrieval service, etc.
By using dependency injection and breaking code into services (repositories, controllers) makes testing a dream, you can test specific parts or a number of parts of your code. I will cover Junit and Mock testing in another section.
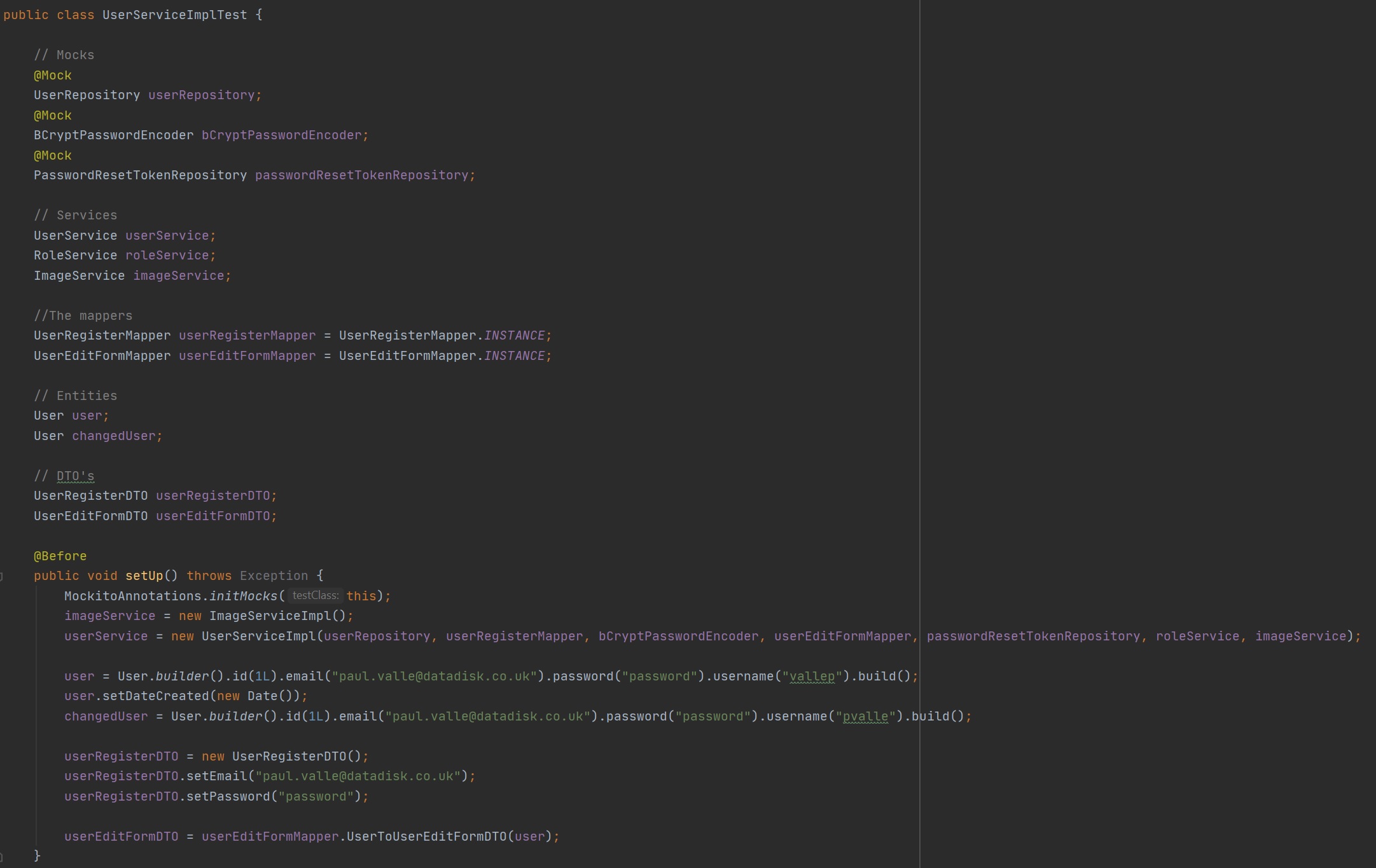
Thats it for services, standard code is use for the CRUD operations and then its up to you to add business logic or create additional services that can be used in your application.