Before we get into the hard code commandline I would like to cover the SAP Hana Database Studio which is an application that allows you to administer and view the Hana database, its a graphical tool that can remotely access and administer SAP Hana Databases.
Download the SAP Hana Studio from the SAP Portal and use SAPCAR to expand it,

Once expanded run the hdbsetup
I took all the defaults
Eventually the application will be installed
When you open the application you will be asked for the workspace details and a master password hints
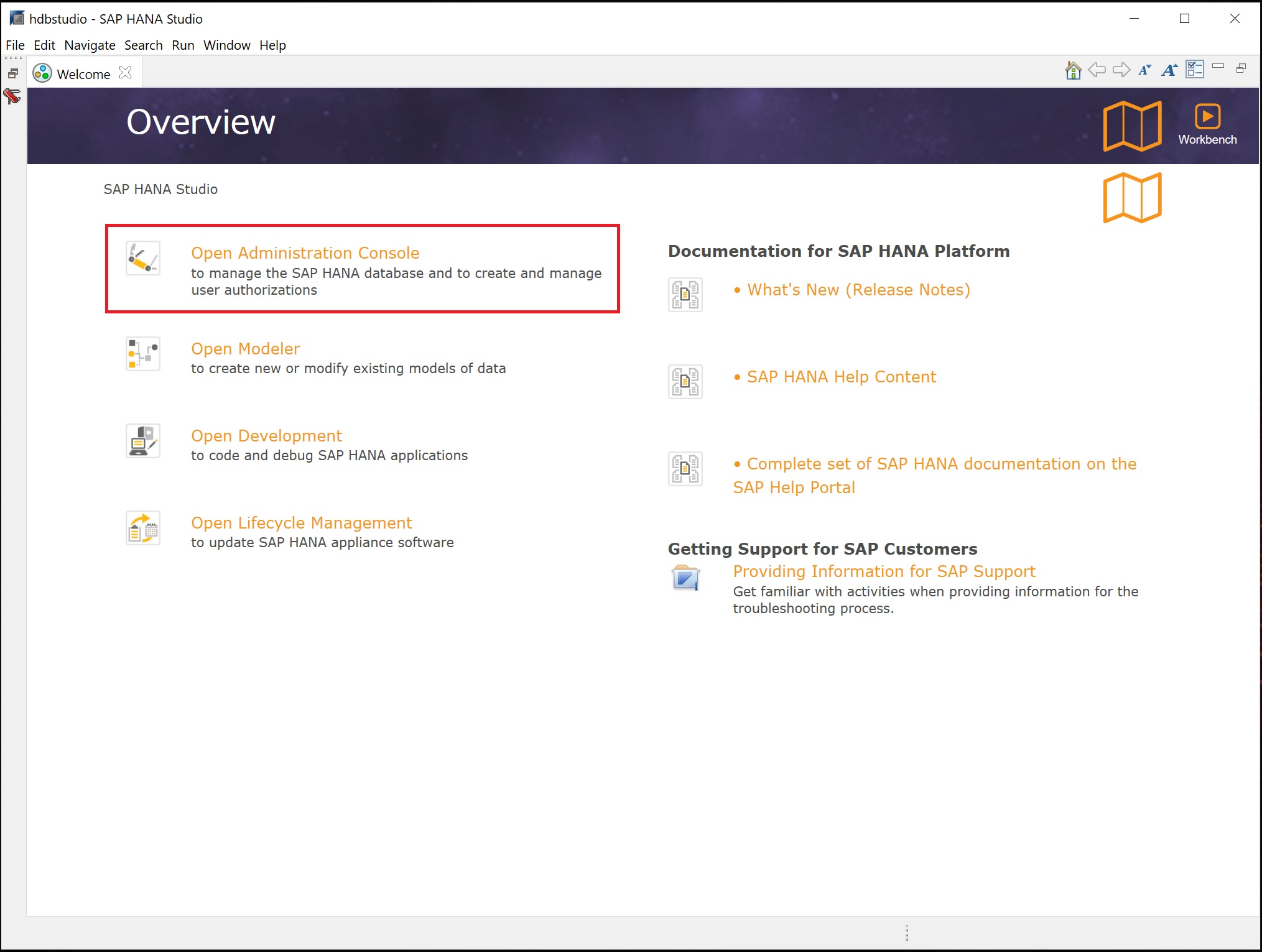
Eventually the studio opens, click on the Open Administration Console
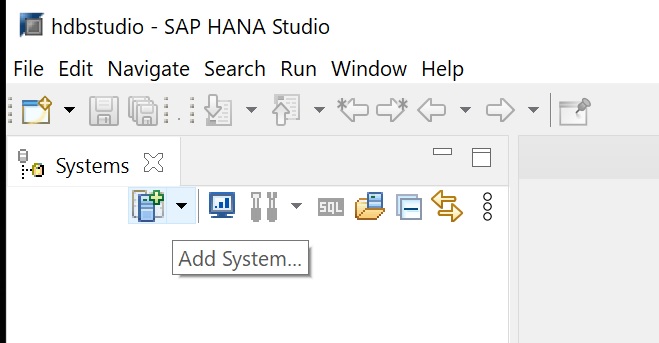
You are taken to main console screen, lets connect our SAP Hana instance to the studio, click the add system button
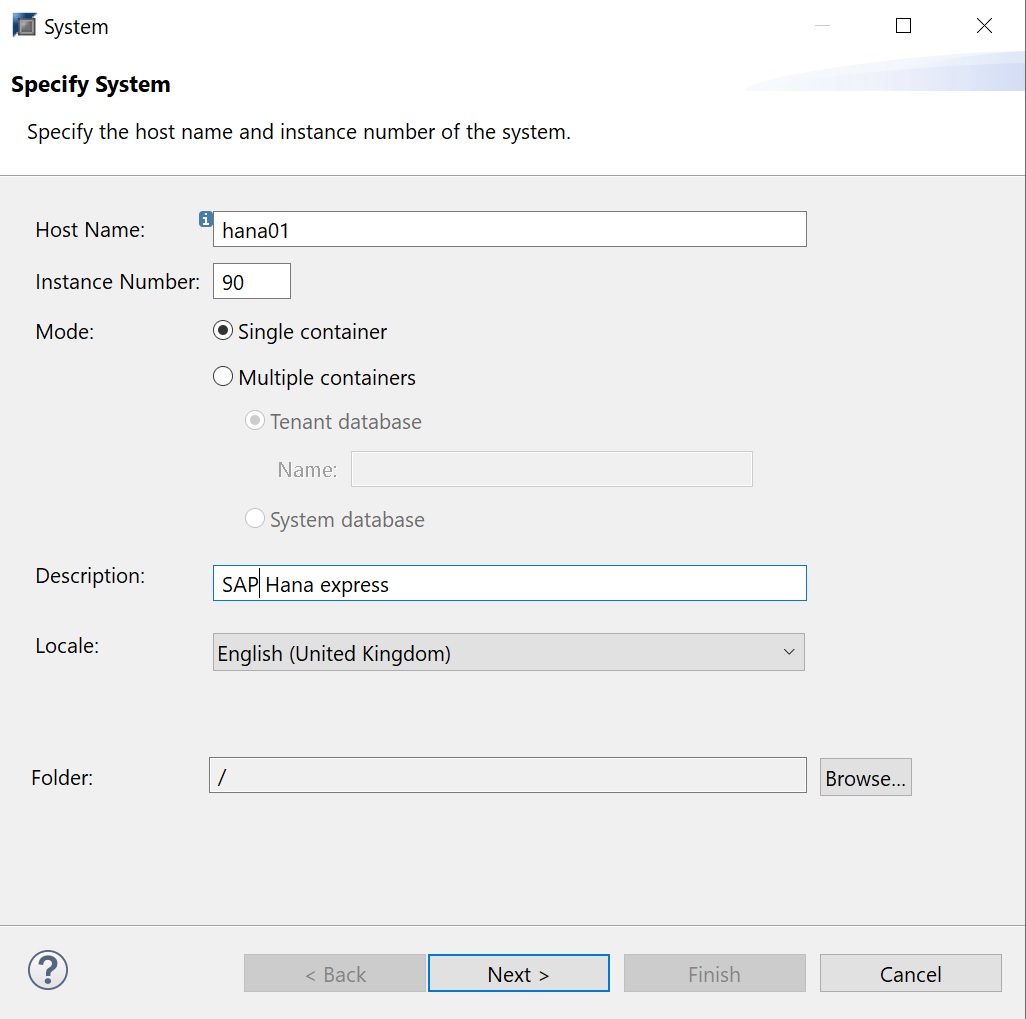
First you can enter a FQDN name or a IP address, select single container, then next
Next we enter the Hana database user SYSTEM and the password you configured during the setup
Once connected you should see a green box and the SID name, the SYSTEM is the username you connected as
If you right-click a number of options are displayed to administer, configure the lifecycle manager (update), backup/recovery, etc.
Select configuration and monitoring -> open administration and the admin page opens detailing lots of information about our Hana database.
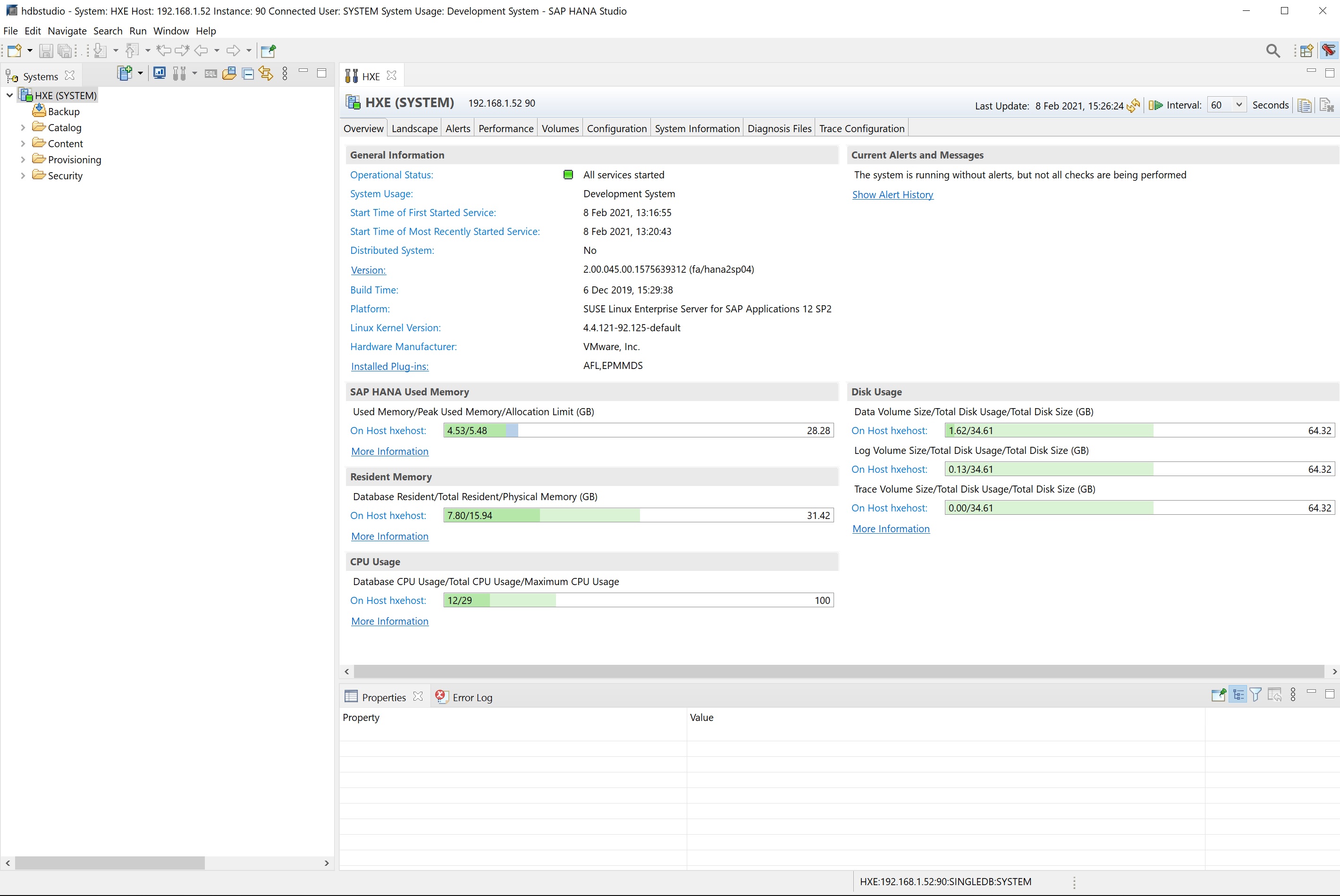
In this section we are going to take a look at the administration side of things, right-click the the system and select configuration and monitoring -> open administration
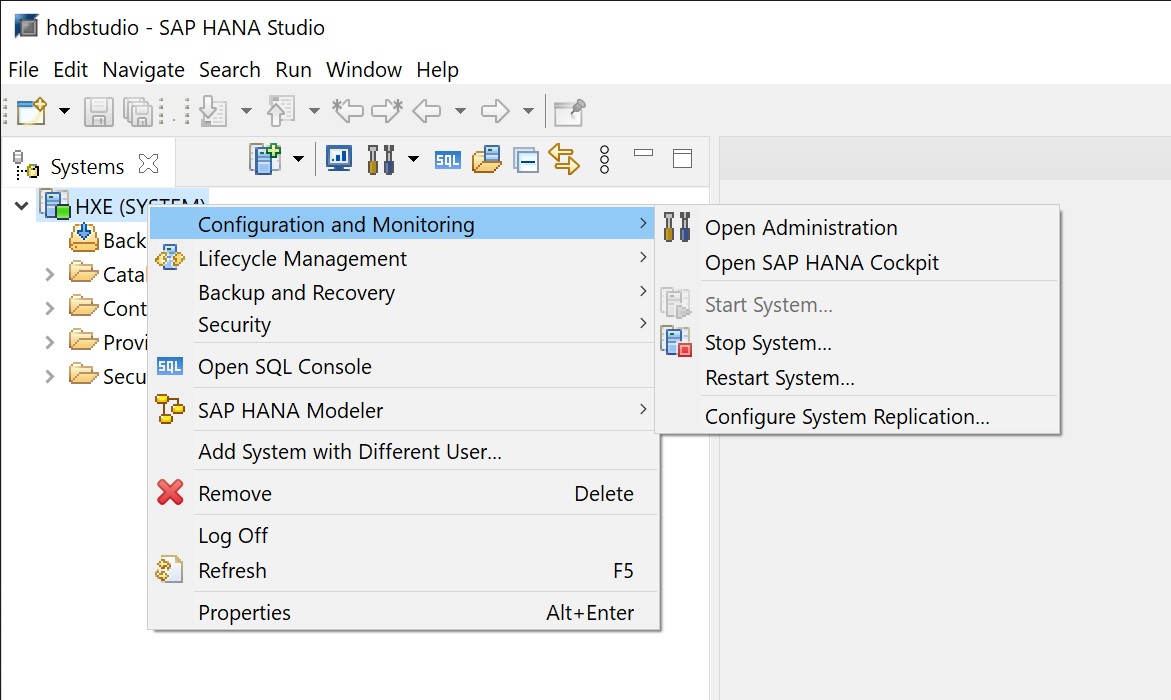
In the admin console there are many options which we will cover, the main screen details the mmeory used CPU usage and Disk usage, this is a good place to start if you are having performance issues with your Hana system. The eagle eyed will notice that the hardware manufacturer is VMware which is correct as I am running on a VMware platform. You can drill down in each section but clicking on the more information links.
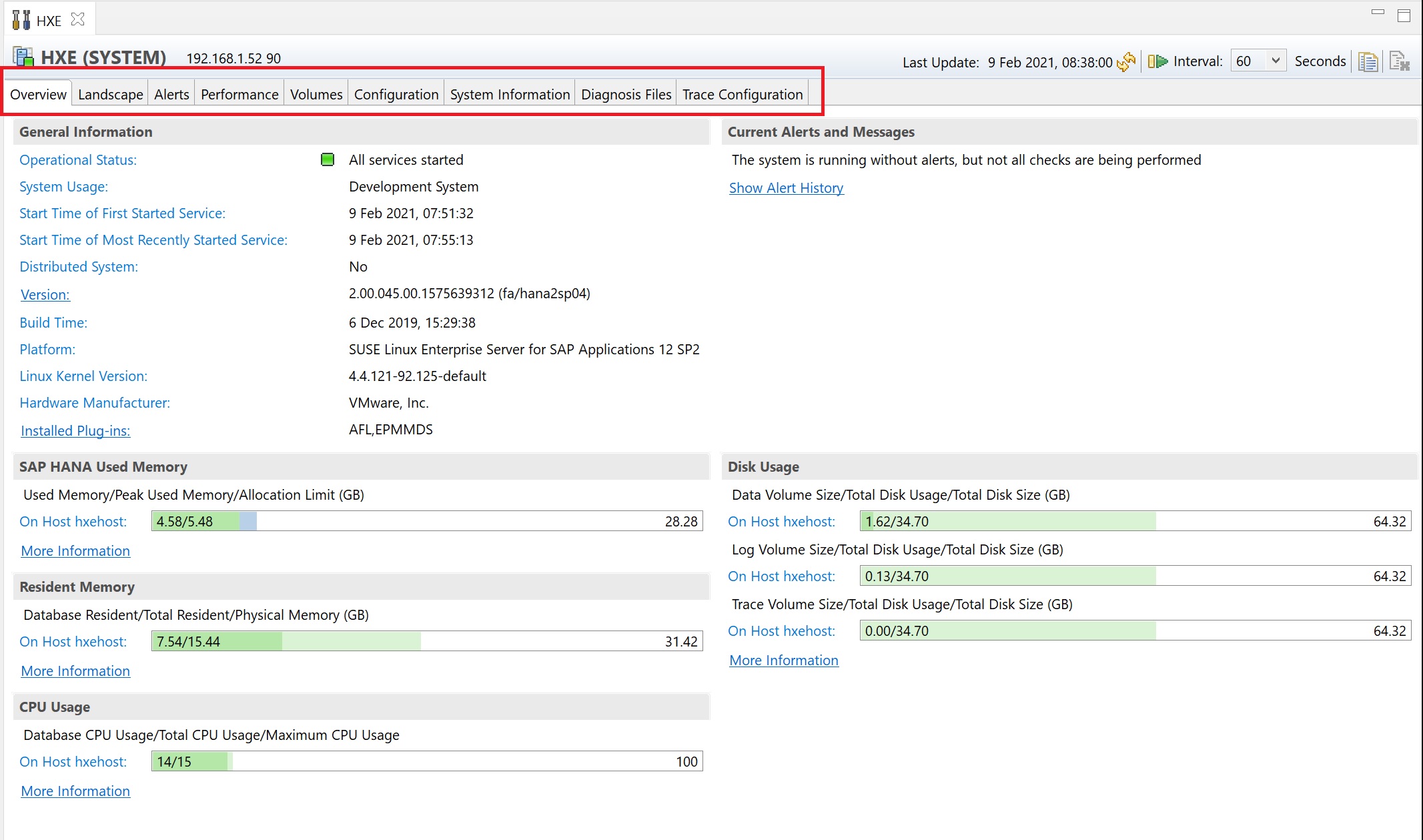
Next we take a look at the landscape tab, here you can view services, hosts redistribution and system replication (if configured), the screen below details the services that are runnign and the resources that they use, keep a close eye on the peak column which will indicate if you need more memory
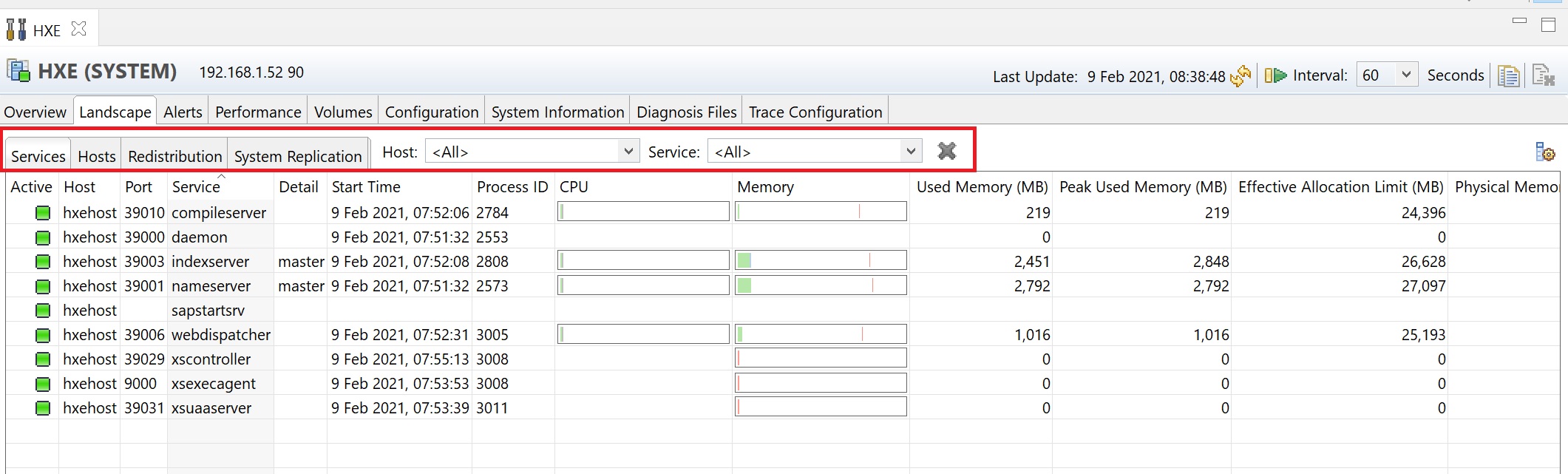
Loking at landscape -> hosts we can see the host details, this screen becomes better when you have multiple hosts connected, especially if using replication.
The alerts screen details any alerts that might have occurred while the system has been running, this is ideal if issue happen overnight
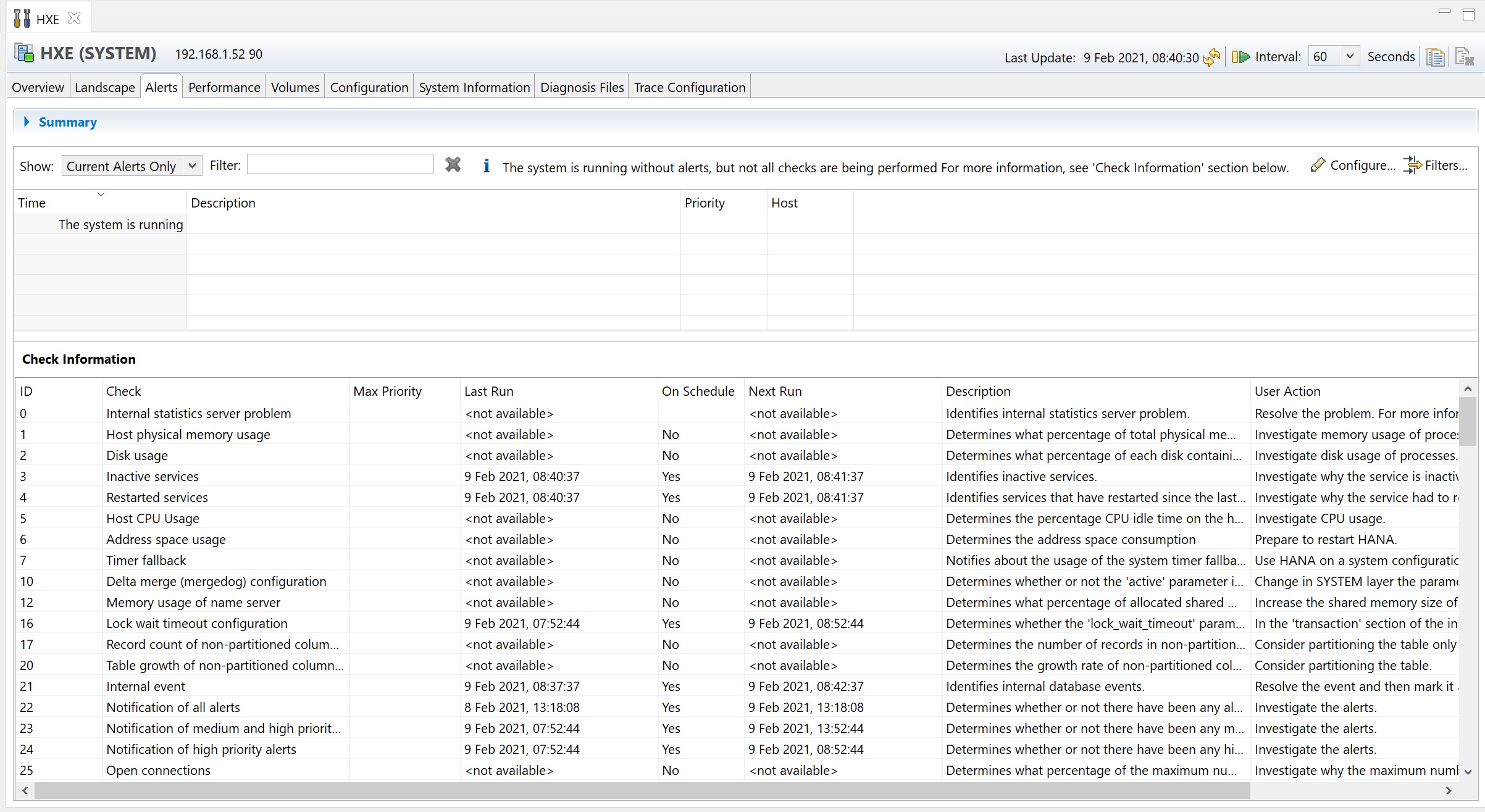
If you click the configure link you can send the alerts to an email address using SMTP, which enables you to see issues more quickly
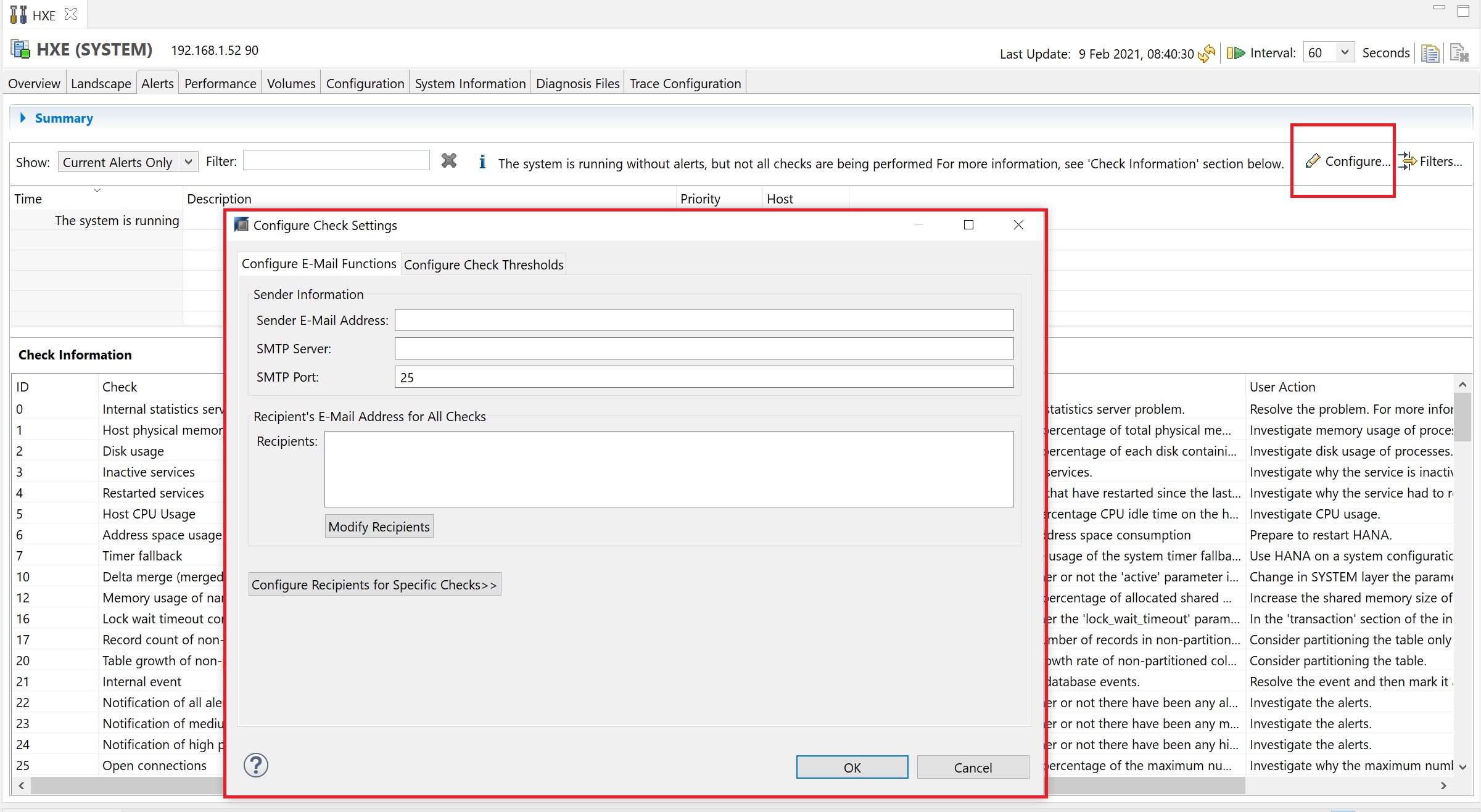
The alerts screen has a summary drop down at the top to give a summary of the alerts types
Next we look at the performance tab, here you have multiple tabs inside it to view threads, sessions, block transaction, etc again this can help with performance issues.
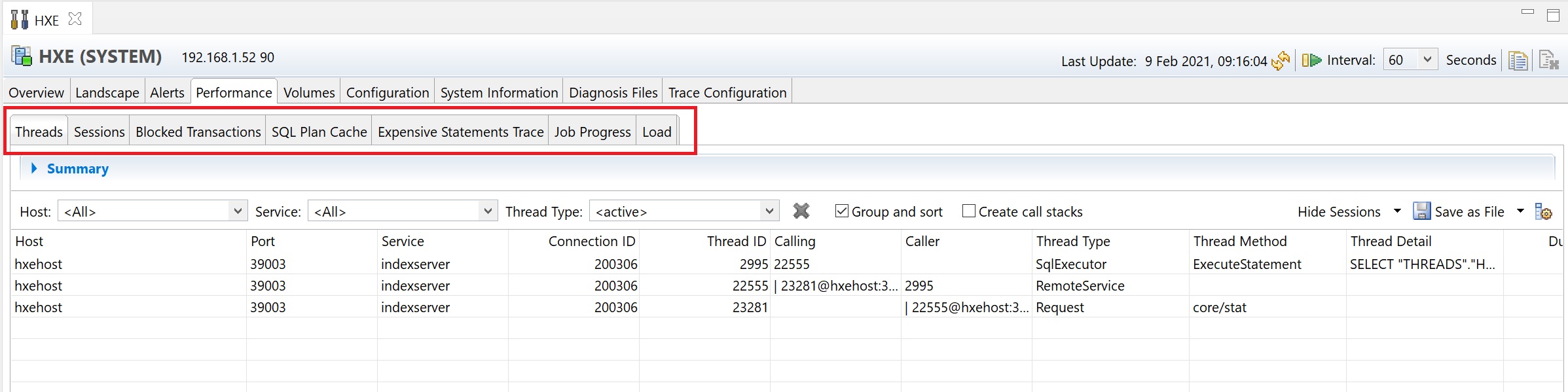
the performance -> session details the session that are connected running tasks, etc, you can scroll along to get more information on each session and to identify problem sessions.
performance -> block transactions are a good place to look for transactions that are locking tables and how long they are locking them, this could be that an application has gone wrong, etc.
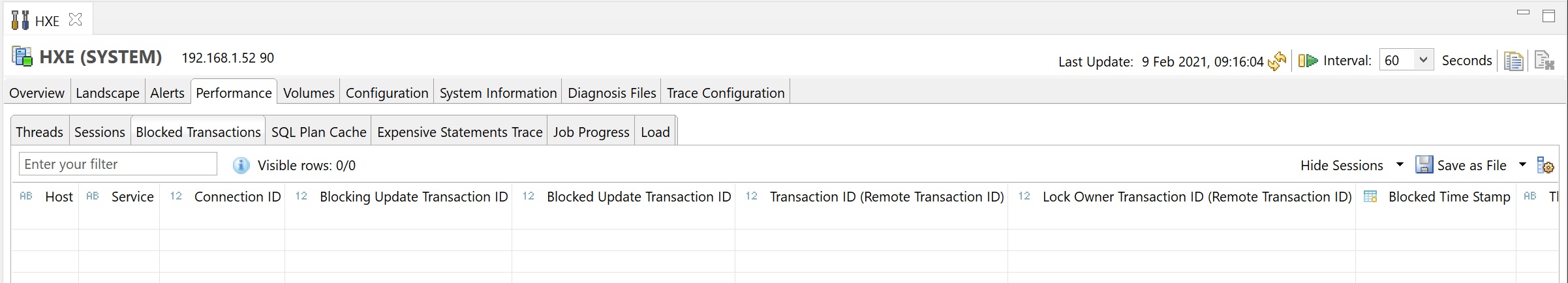
Next we look at the volumes tab, here you can see they data and log volumes that make up the Hana system, here you can see the path on the linux system plus the size, at the bottom you can obtain I/O statistics however generally we use SAN's now and disk performance is better lloked at from the SAN's own tools.
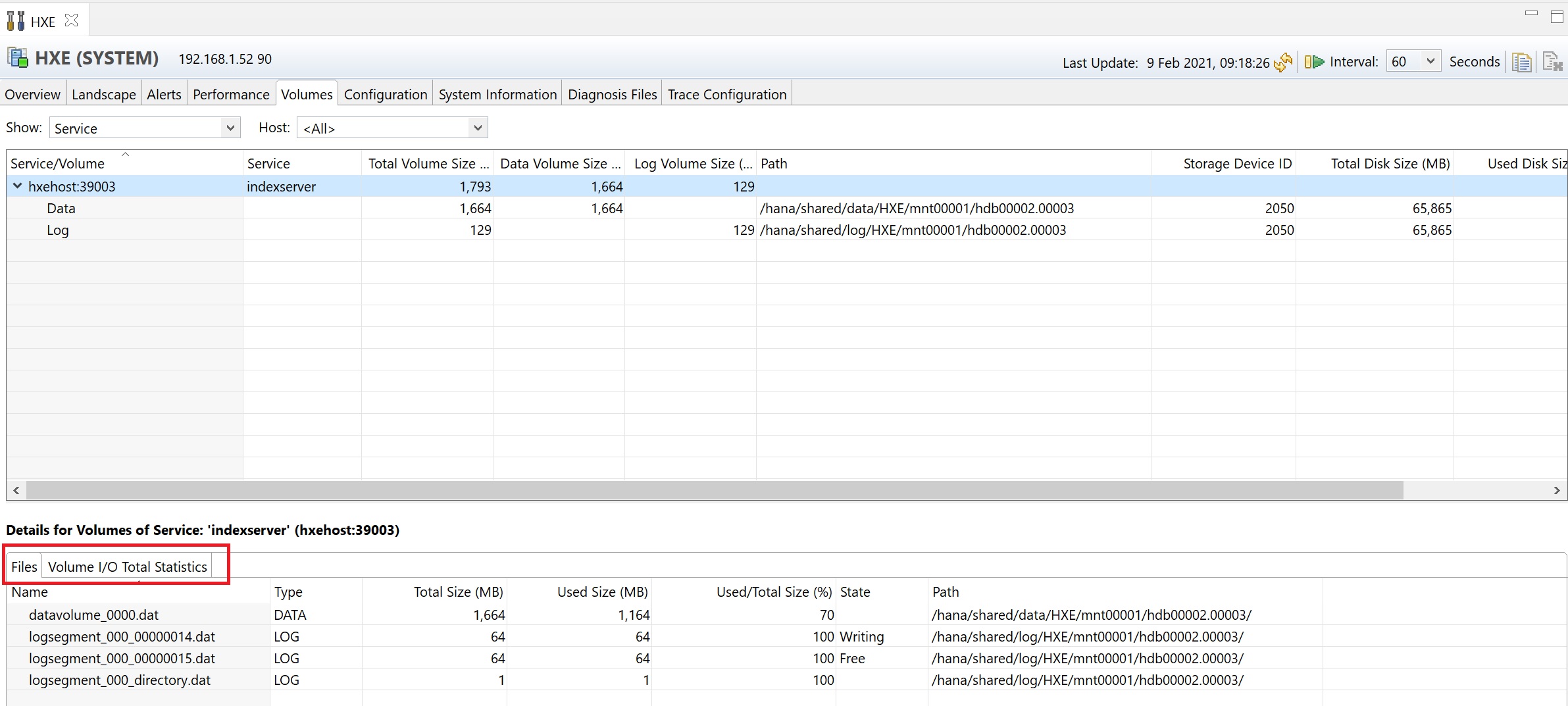
The configuration tab details the system parameters, if you need to perform any tuning this is the place to come, generally you will be advised by a SAP Note or SAP themselves to change any parameters here
The system information tab has a number of predefined SQL commands that can be used to obtain system information
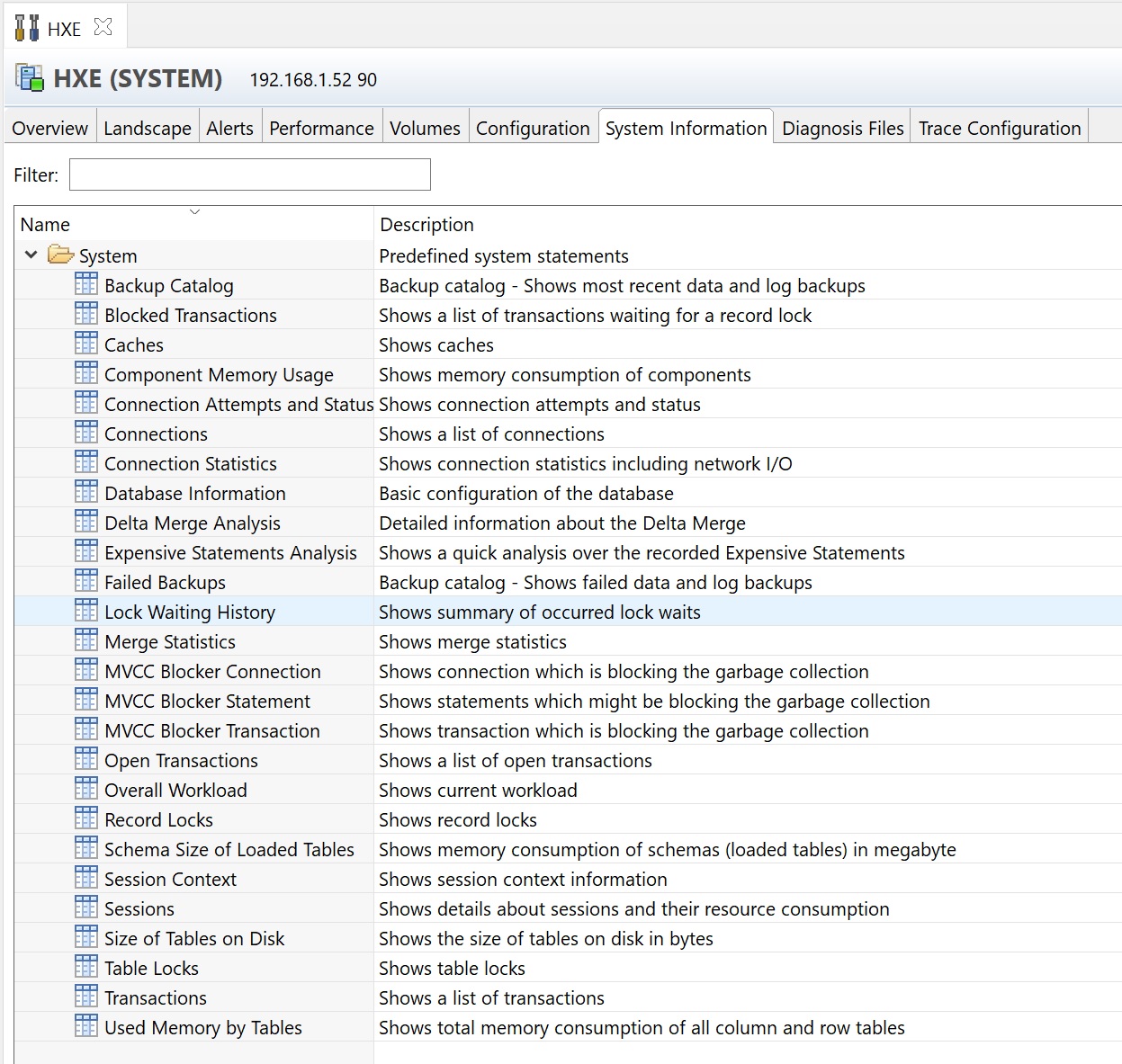
By selecting (running) one you are taken to a results screen, here you can see that I have run the show list of connections
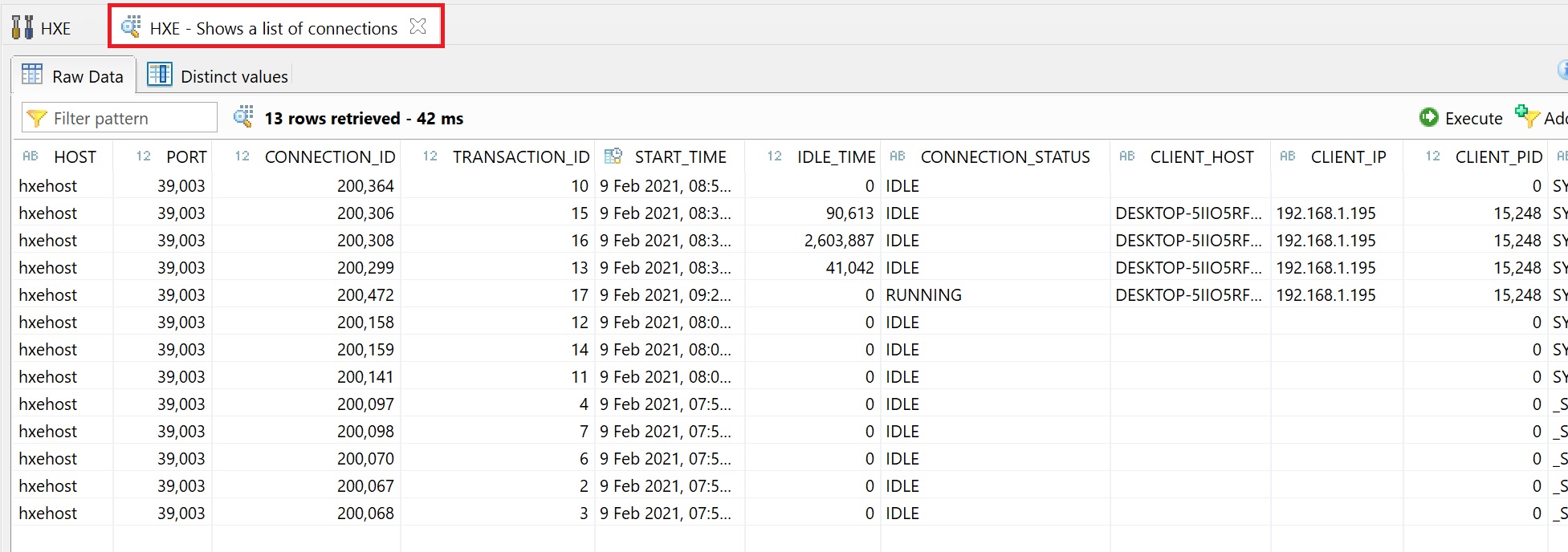
The diagnose files are the trace files, here you can collect data and view if you have any issues, you can delete or view the collection files
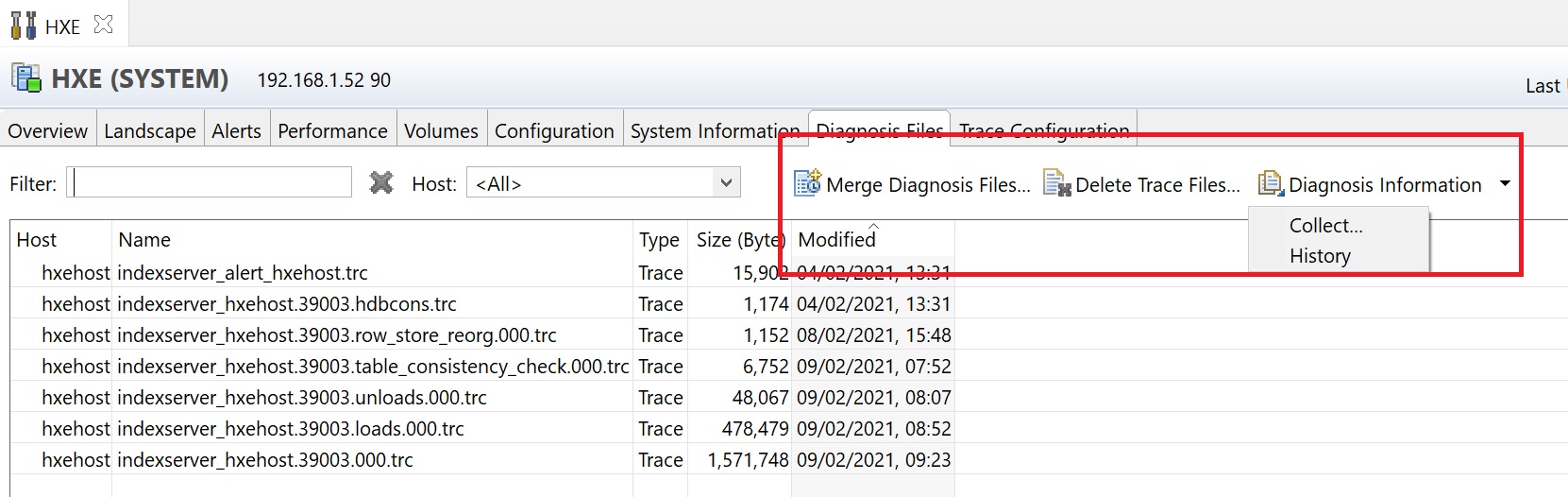
Here you can see that that I am specifying a period of time to display.
Lastly we come to the Trace configuration here we can start tracing of specific areas if we have any issues hoping that you can capture the issue in question. However once you have finish make sure you turn off tracing as very large files can be created.
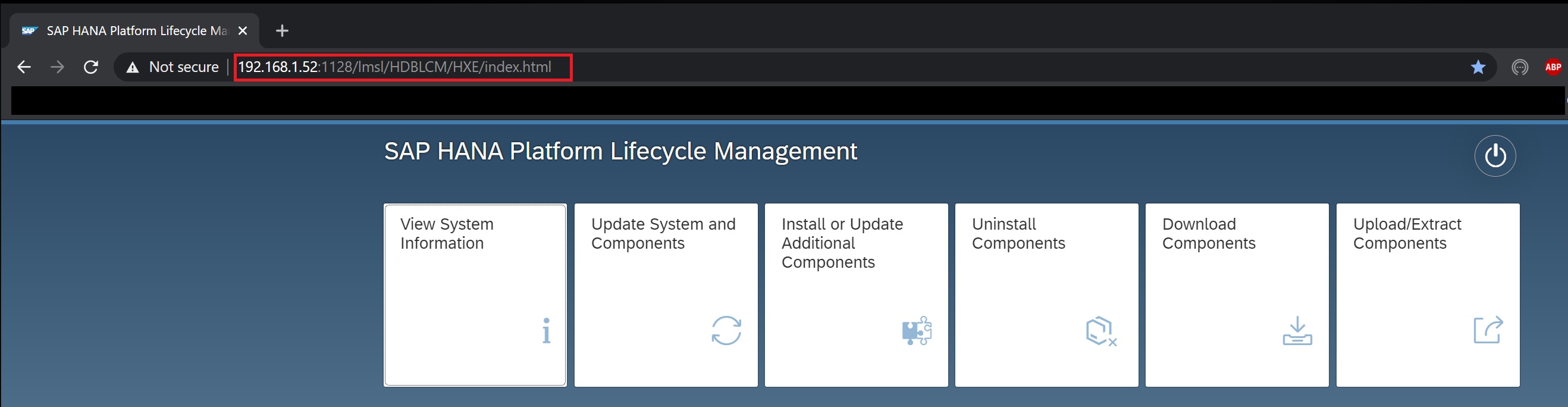
The lifecycle manager basically allows you to check if the system has any updates, and to apply them. I had issue accessing the lifecycle manager from with in the Hana studio, however you access it using the URL https://<server ip>:1128 (or port 1129). As you can see below it uses the new Fiori apps, here we have a number of options
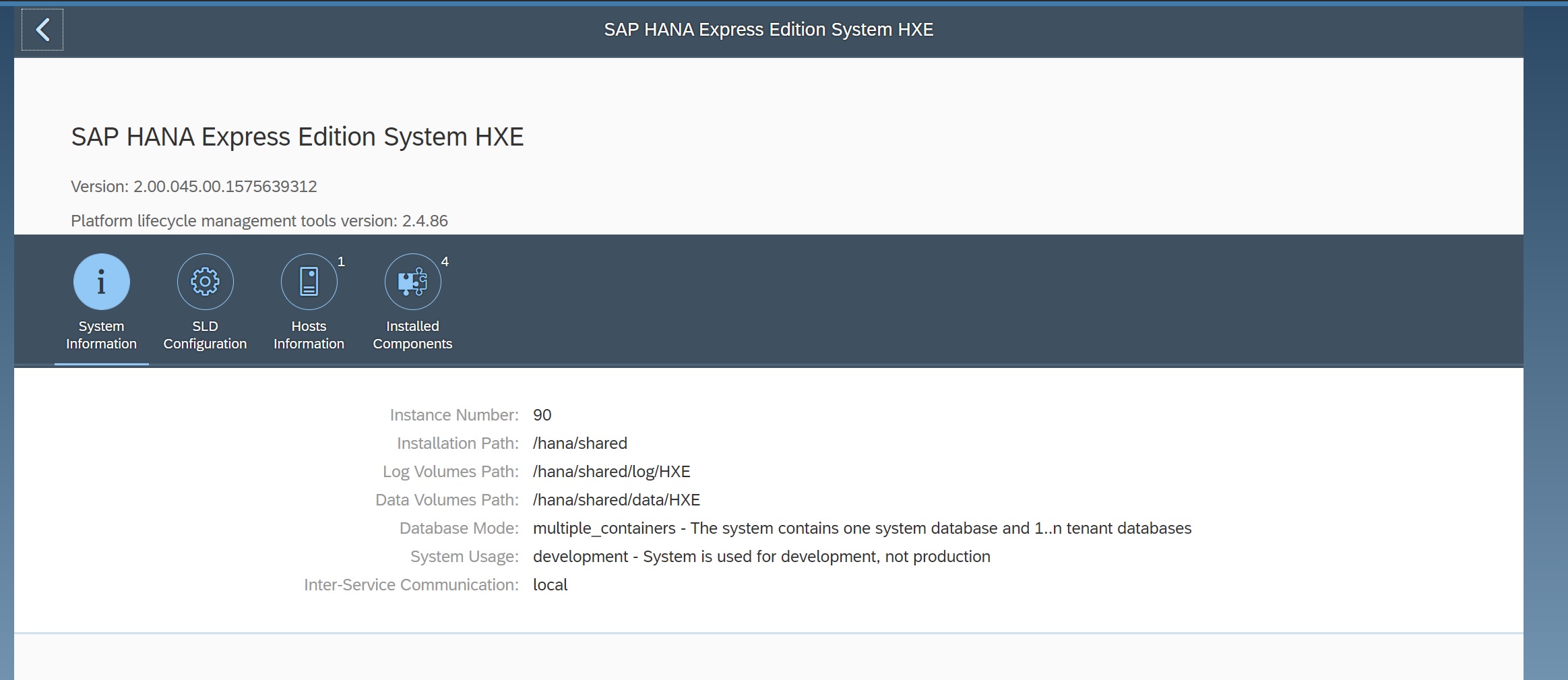
The view system information details information about the current system
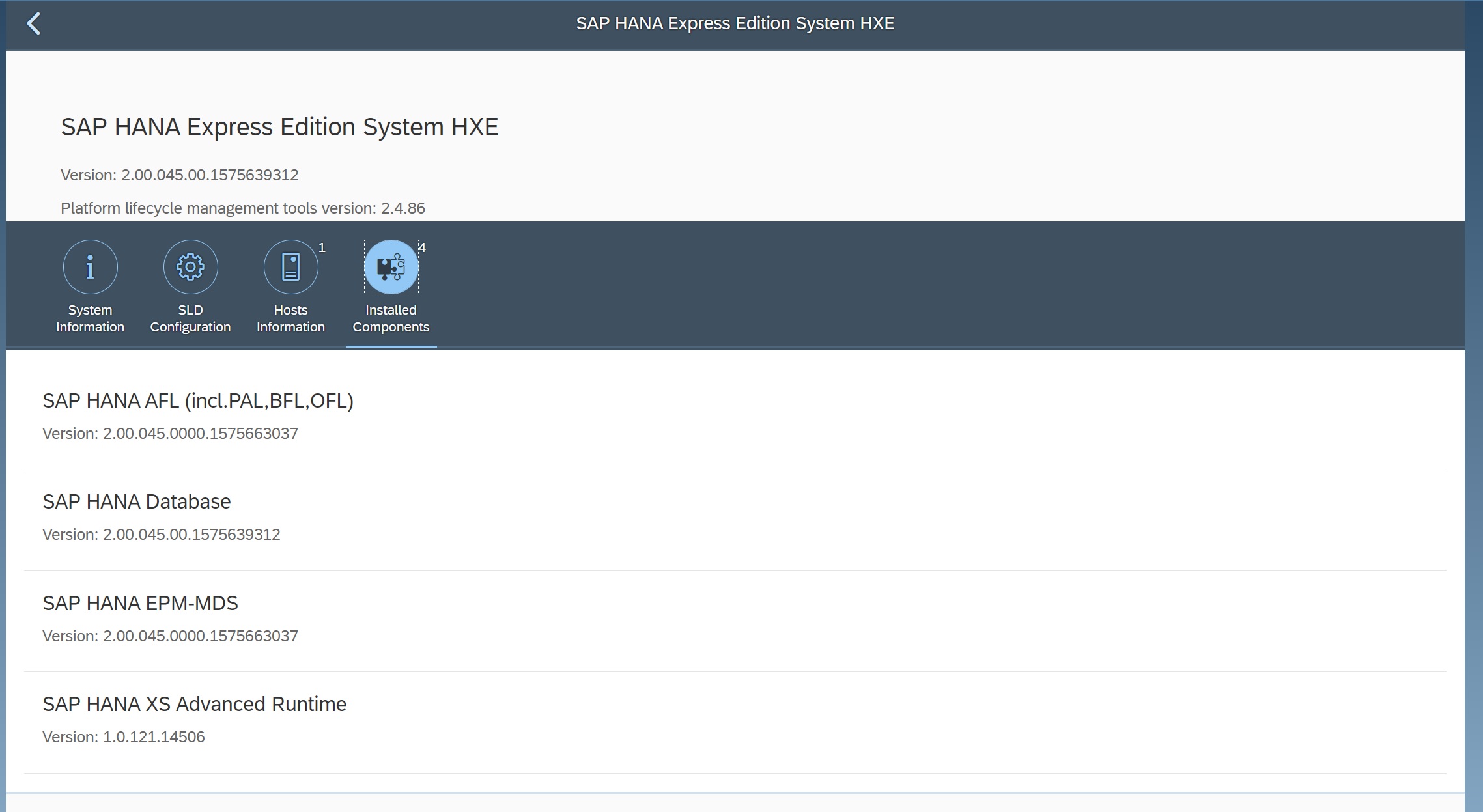
Selecting the installed components displays the components versions
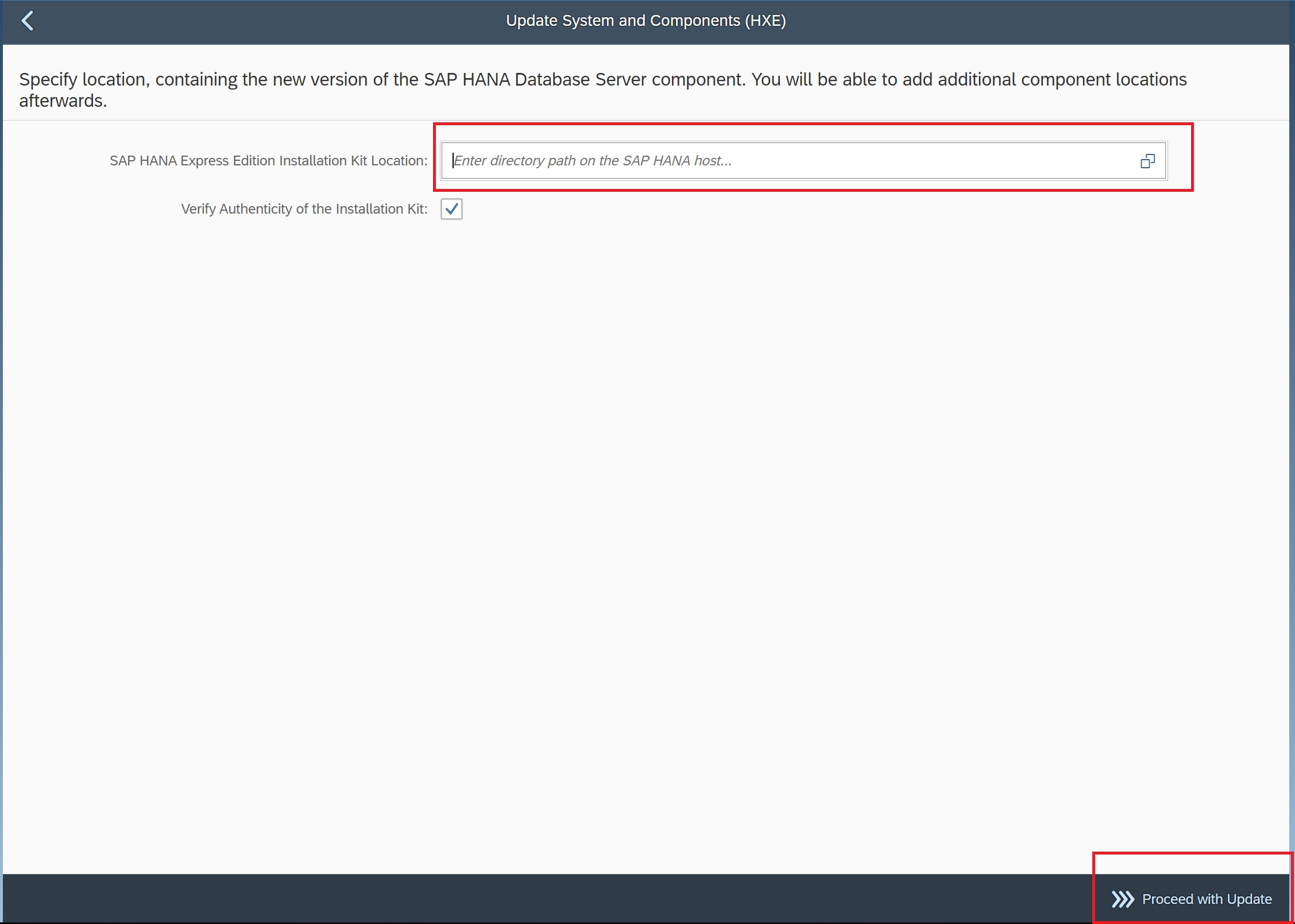
If you have downloaded any updates you can use the update system components button to update the system pointing to the updates downloaded.
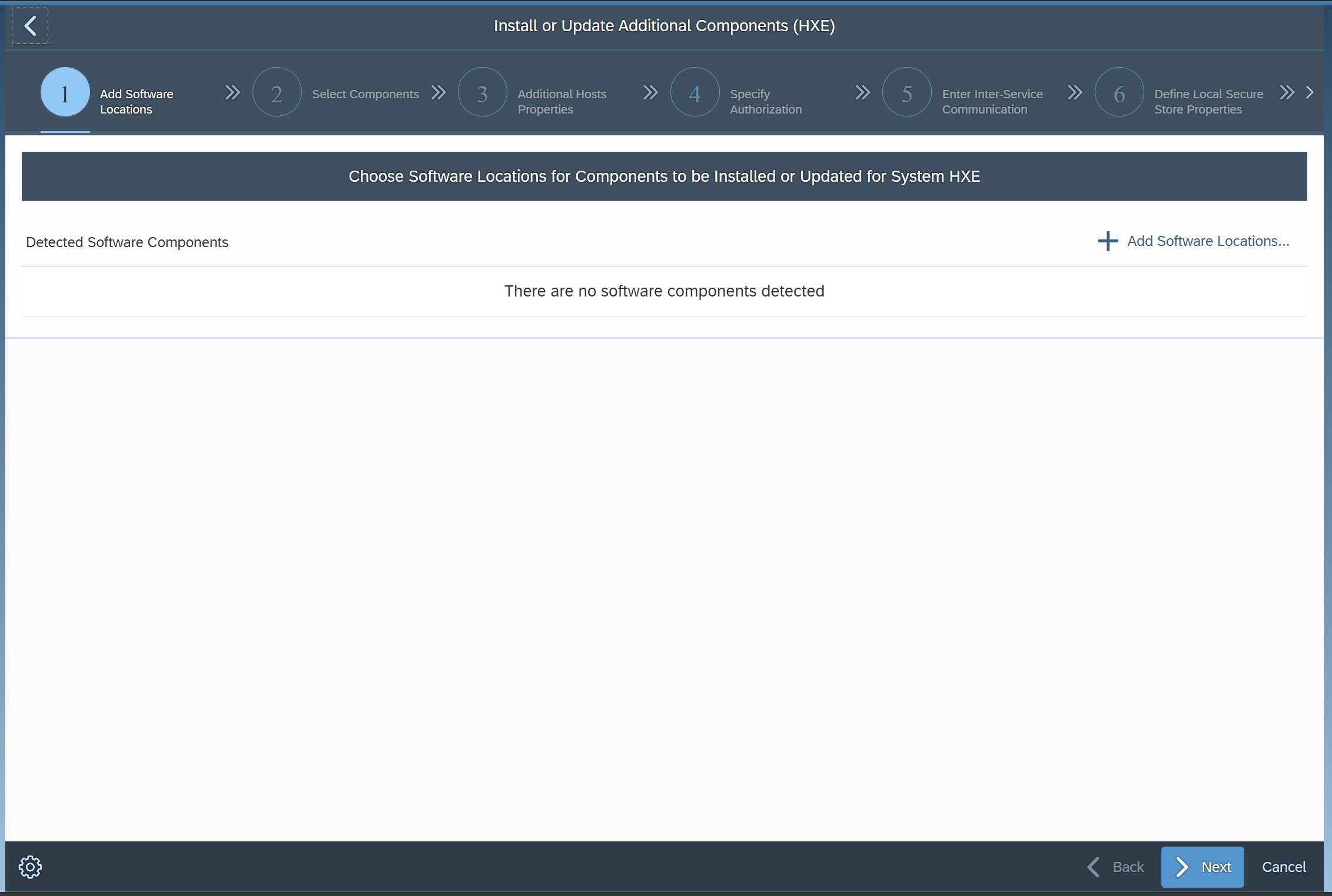
The install or update additonal components allows you to install additonal components that were not part of the initial installation, again you need to download these components first and then use the add software location button to point to them
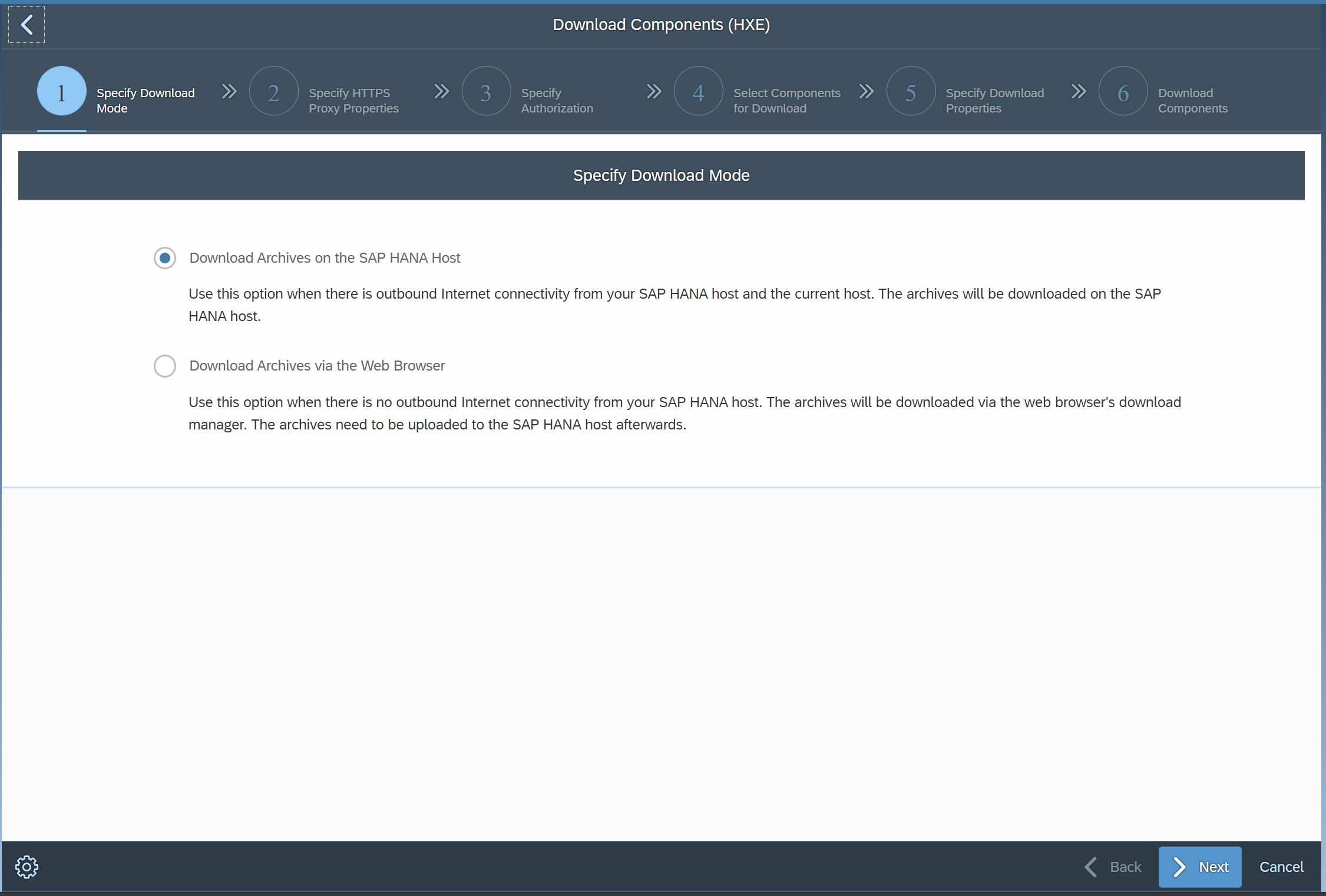
The download components automatically check you system to see if there are any updates that can be dowenload and thus installed,
Select the component that you wish to update
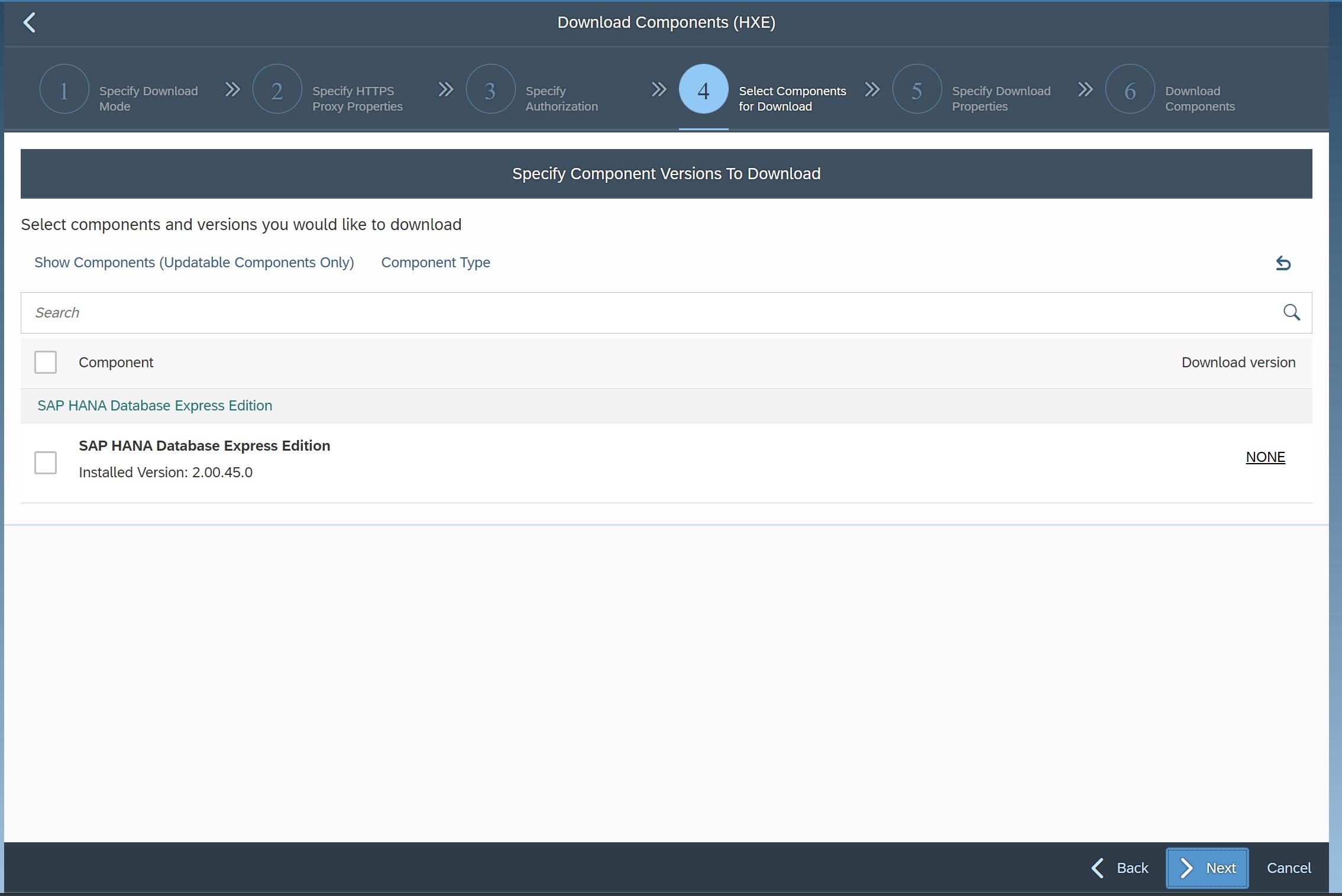
The download should then download any compoents that need updating, how I had a libssl error as i needed to update to version 1.1 (1.0 was installed).
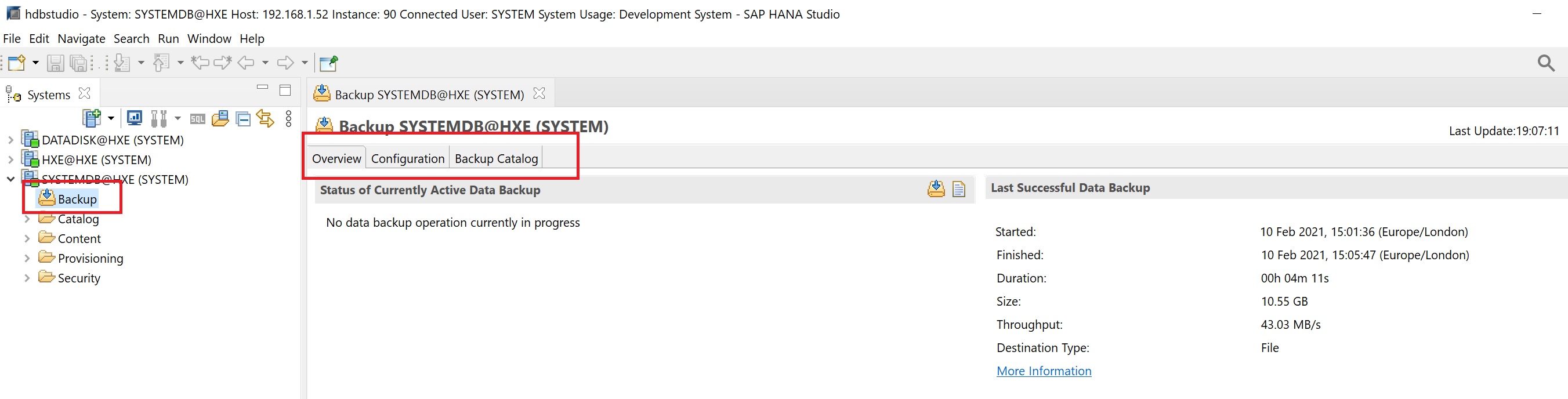
Returning to the Hana studio and right-clicking the system and select the backups, you are taken to the main backup screen, here we have three tabs the main backup screen, the configuration screen and lastly the backup catalog (backup history)
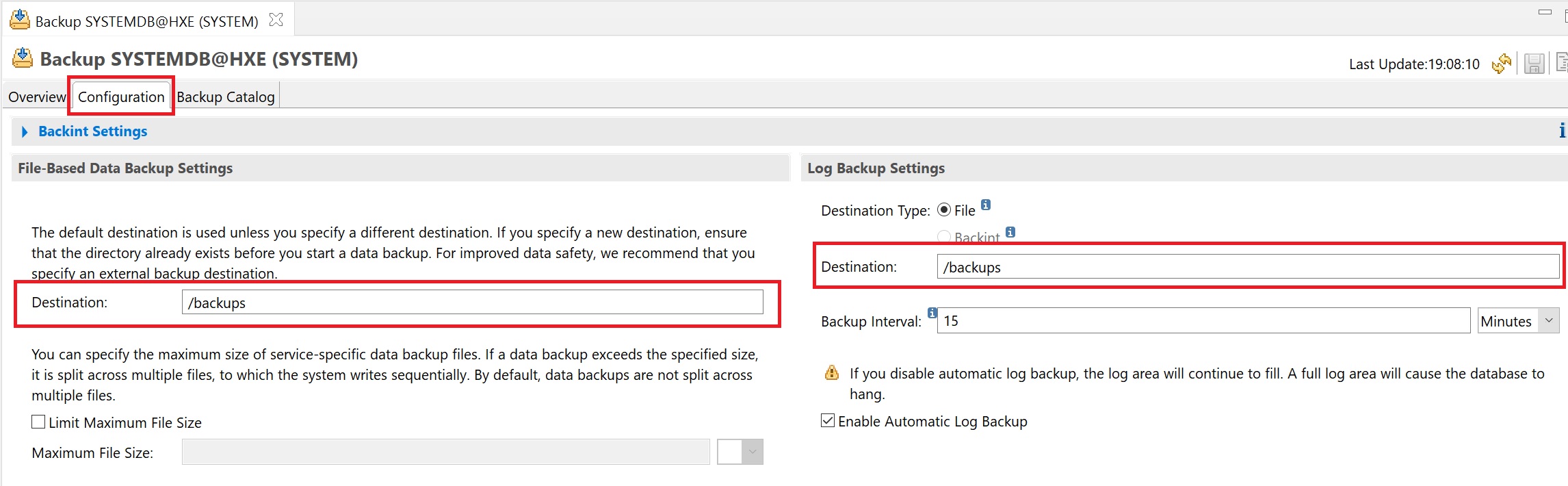
The configuration screen you can set the backup location, the type of back and the backup and the interval for the log, note that this is not where the backup catalog is keept only the actual backup themselves.
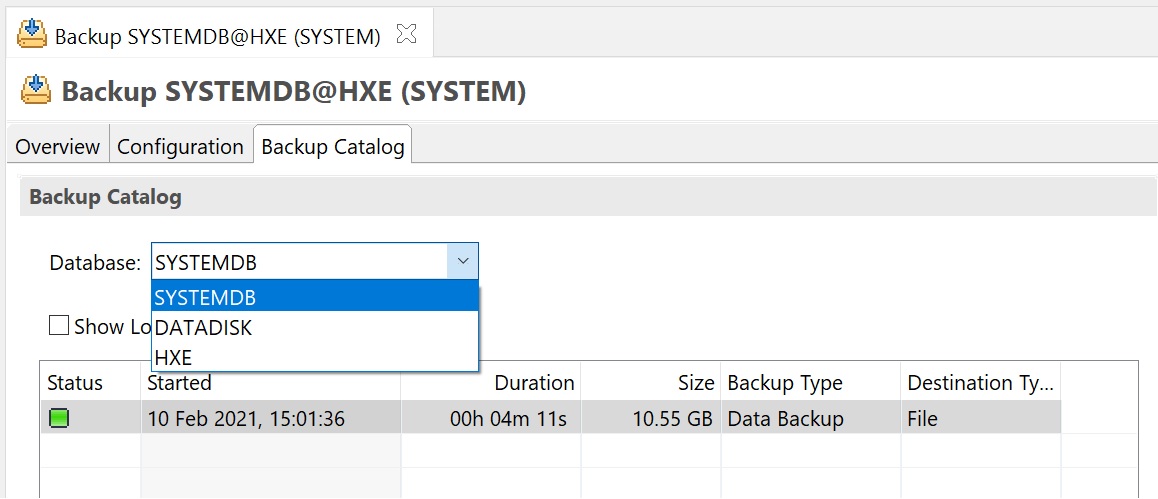
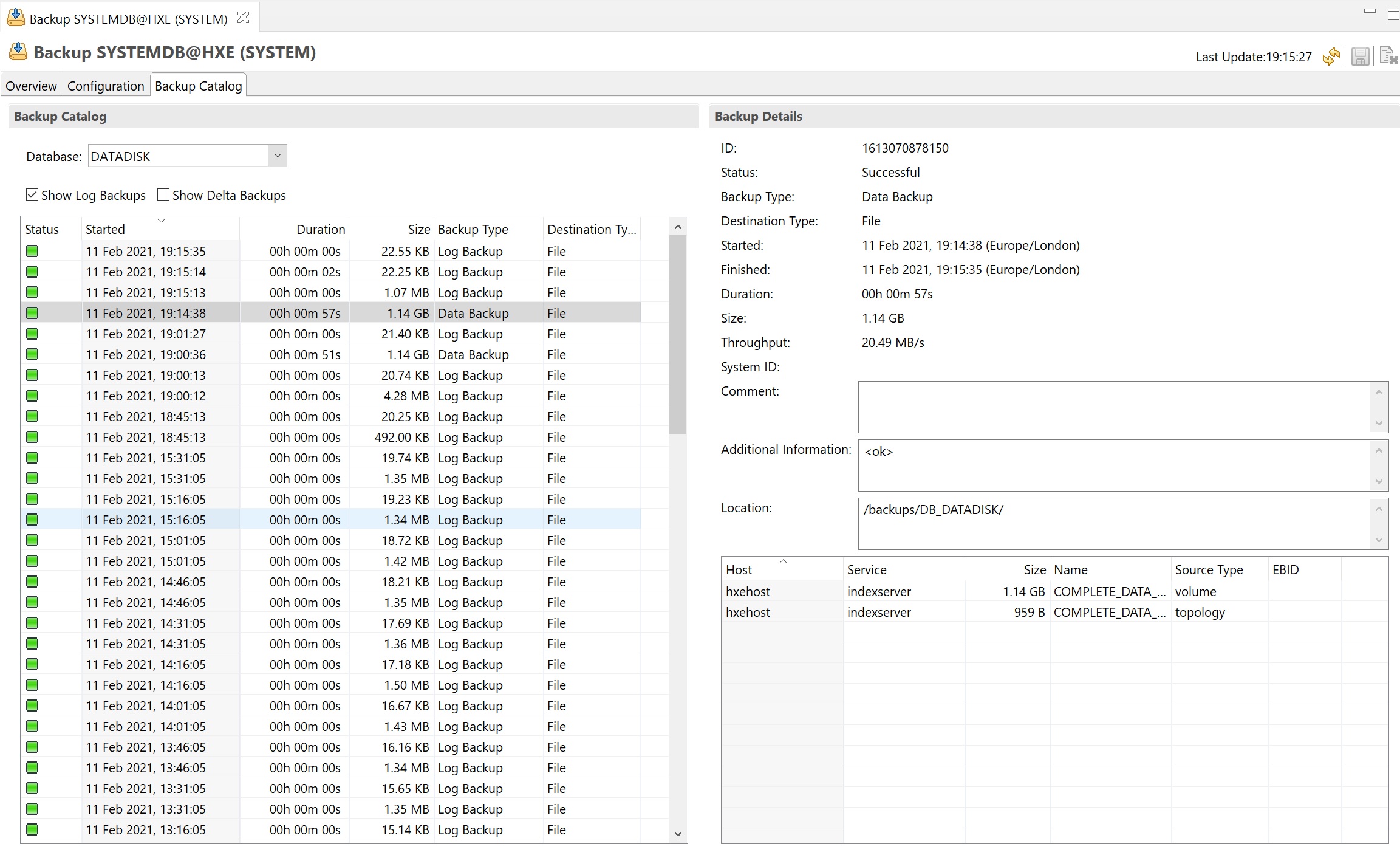
In the backup catalog of the systemdb you can see a drop down list for all the other tennat databases
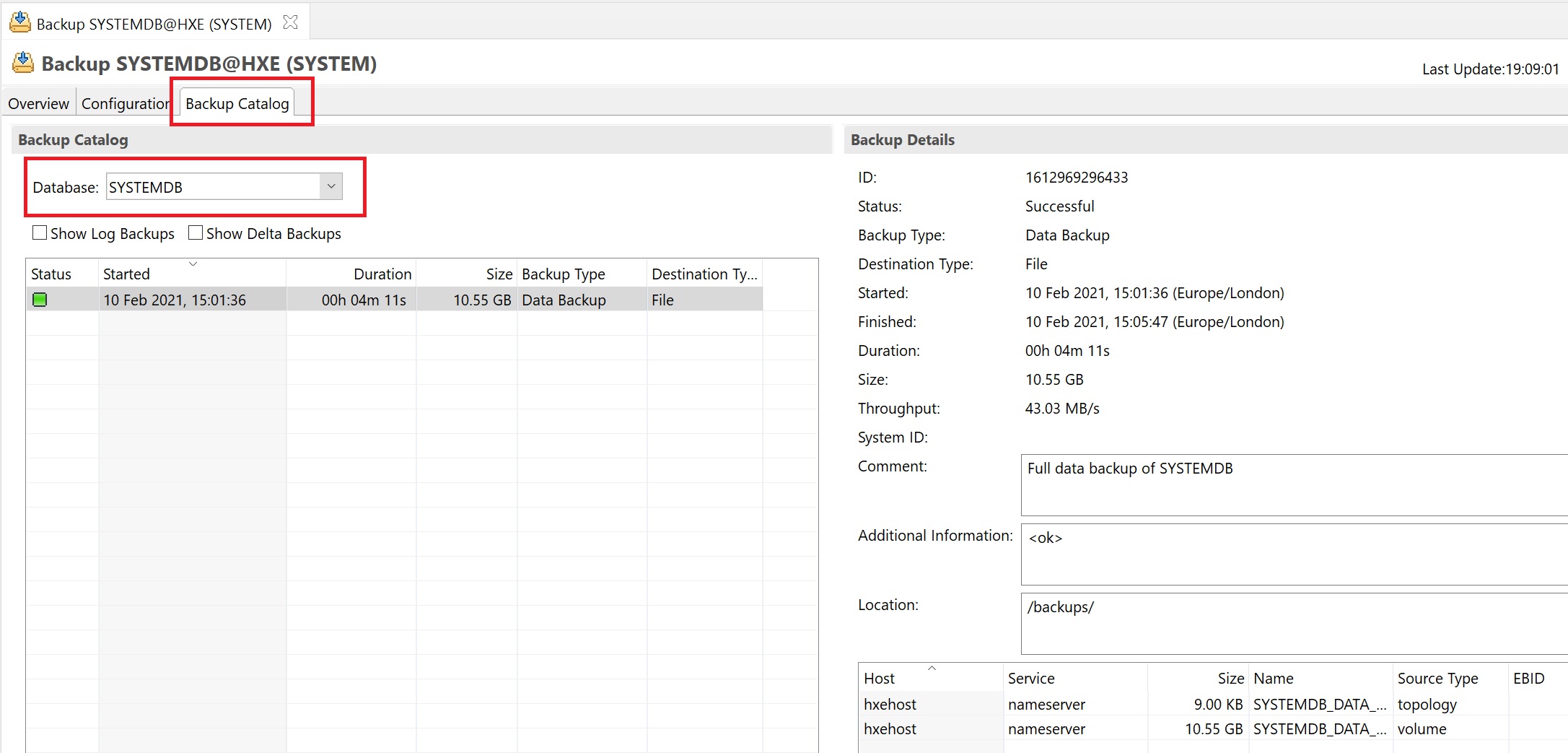
You can see that I havethe systemdb backup and two other tenants.
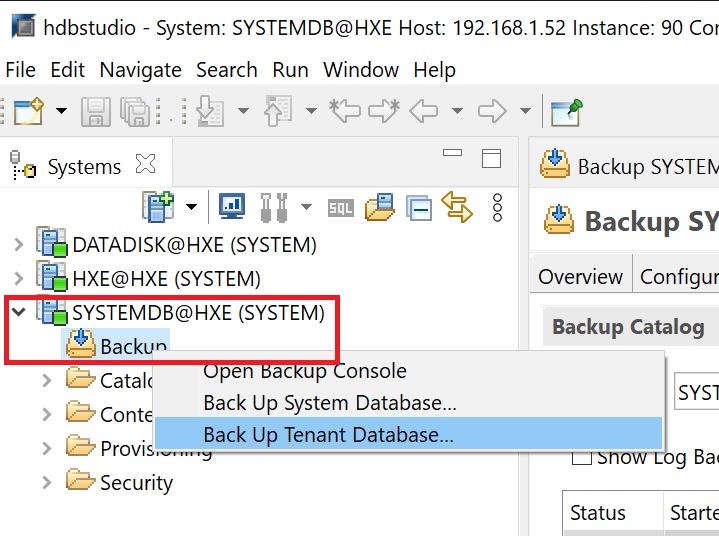
Lets create a backup, double-click the backup icon on the systemdb and you have two backups options system database or a tennat database
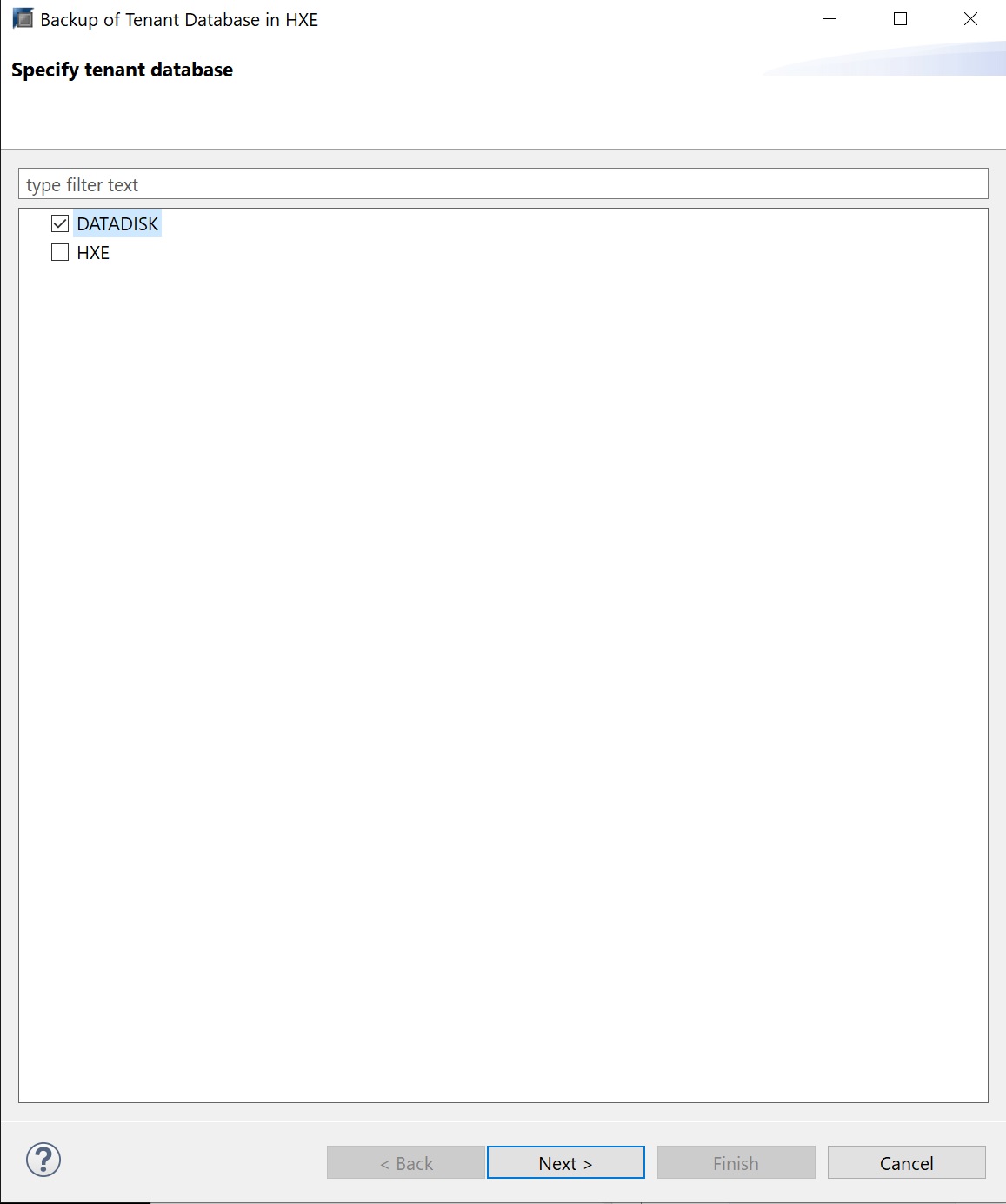
I have selected to backup a tenant, here I have a list of the two tenant databases that I have configured.
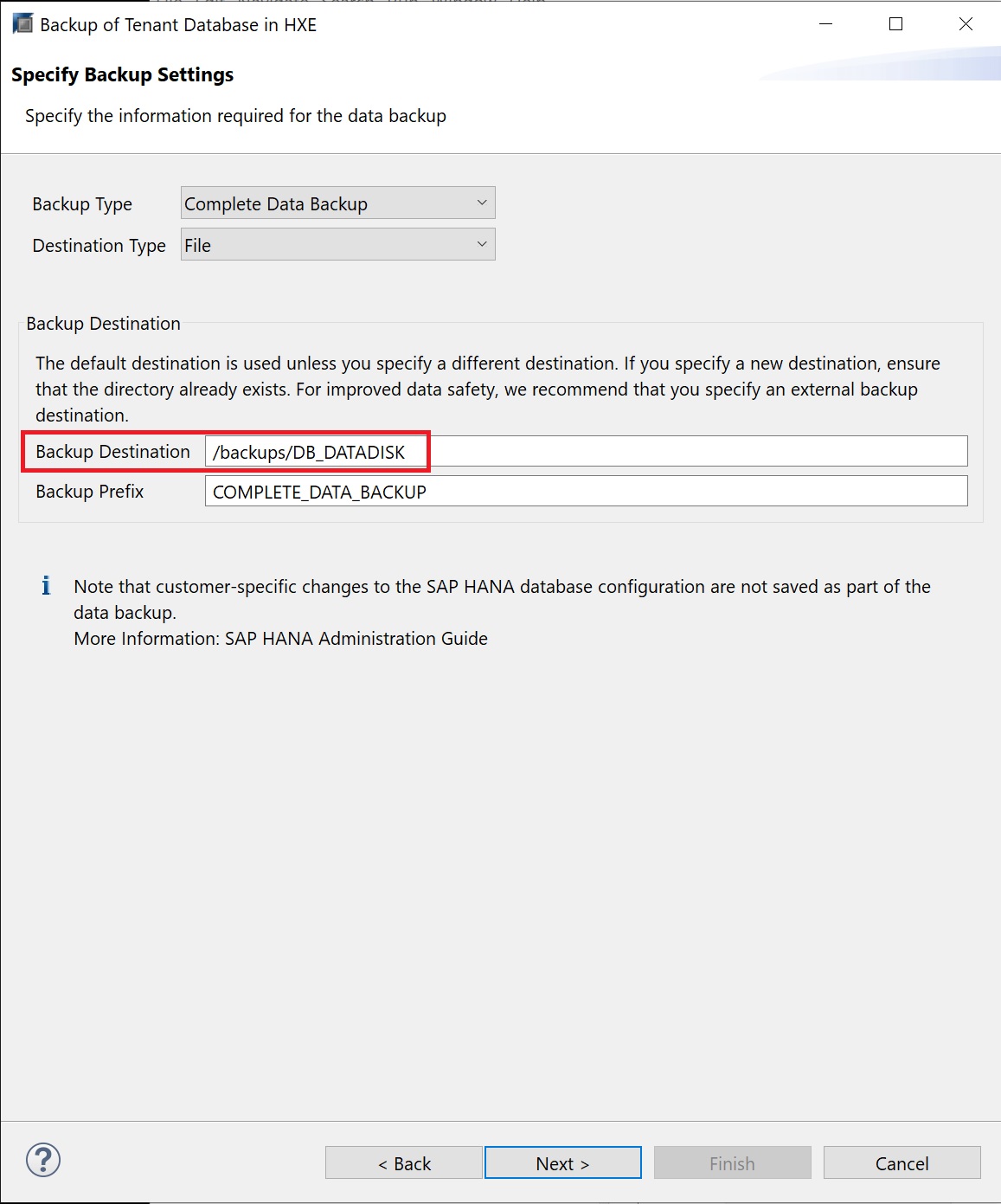
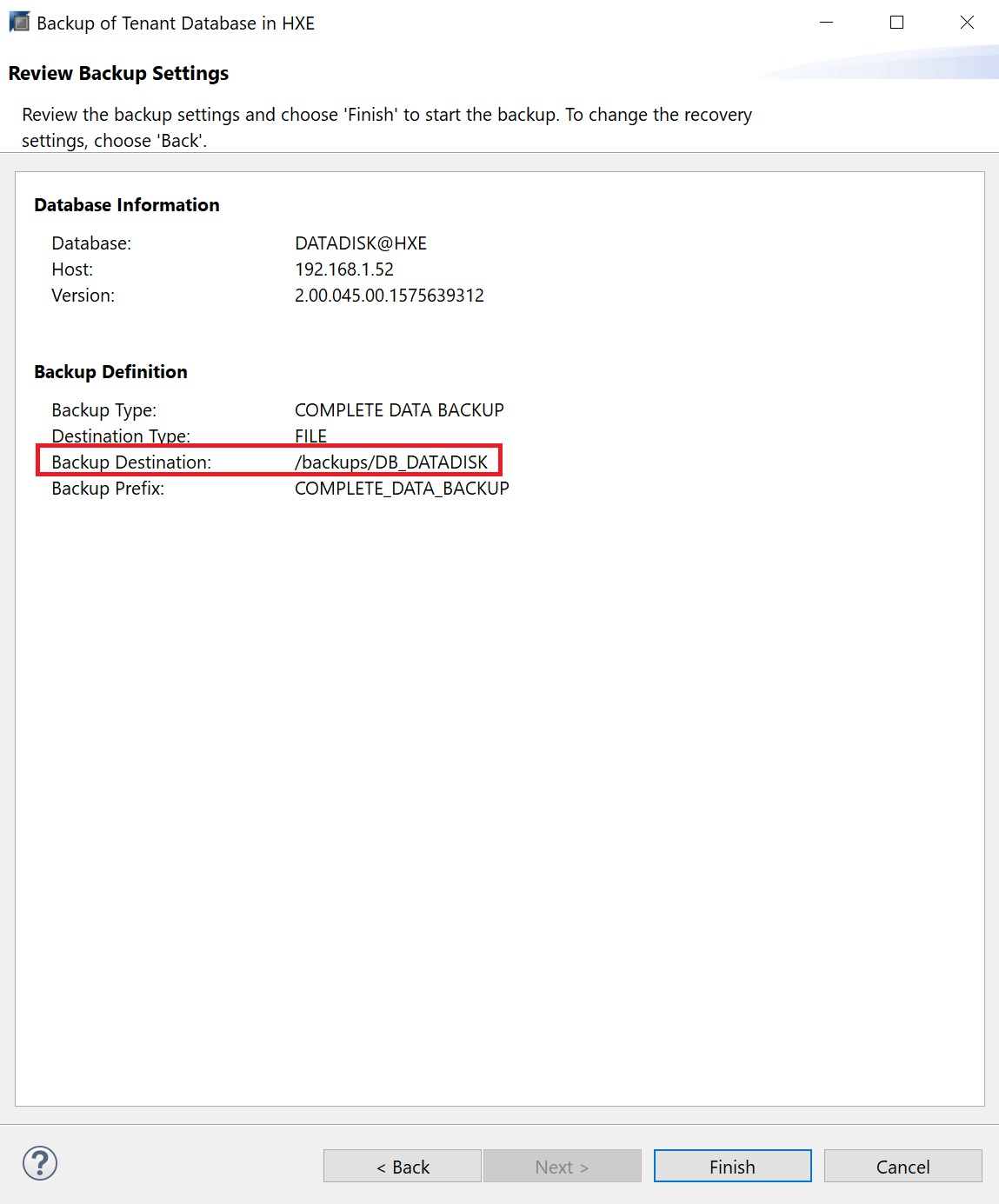
The backup screen lists the type of backup and the location which was automatically filled for me, as you can see tenant databases are backed up in there own directory.
You are taken to the review screen, click finish to start the backup
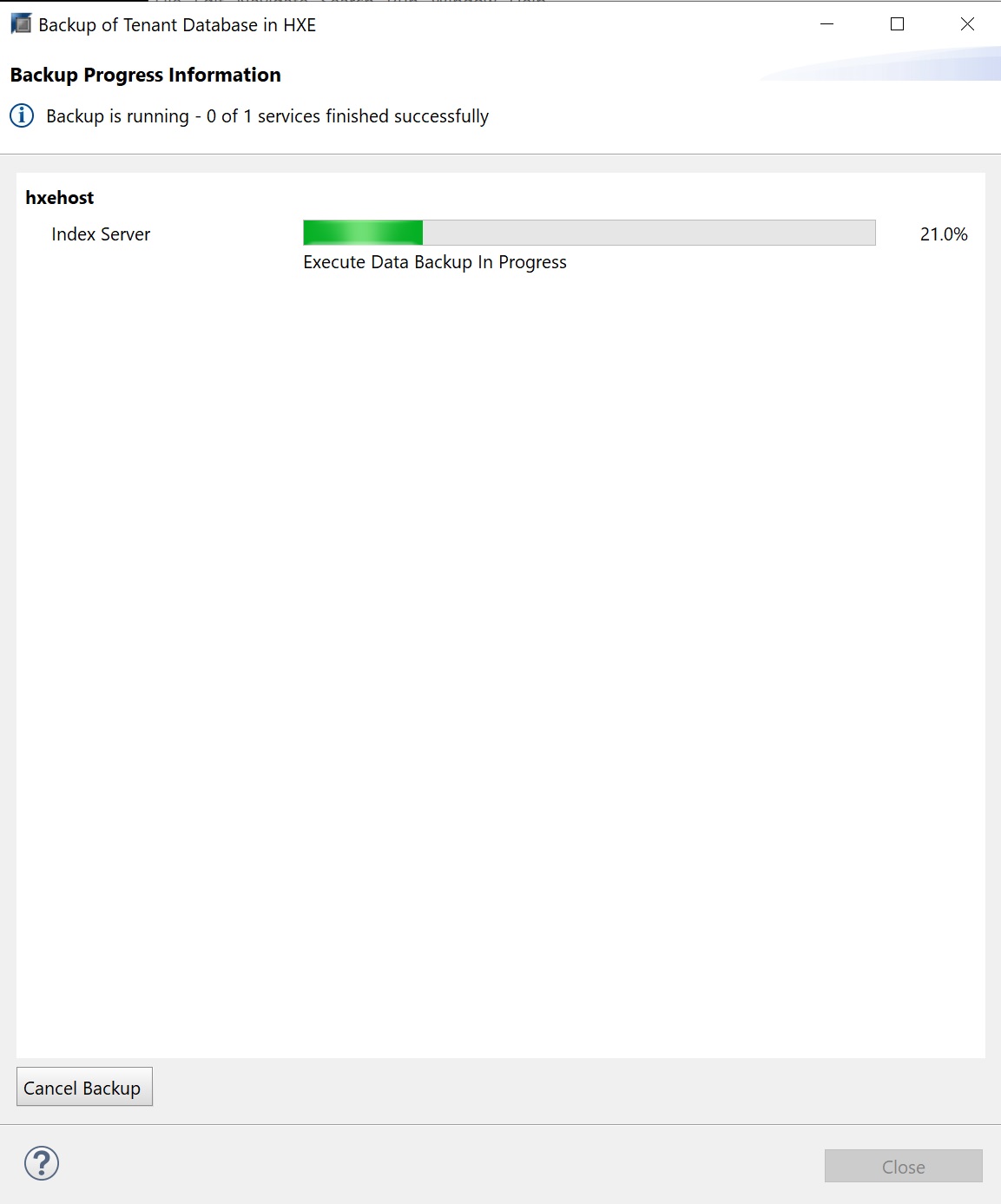
A progress is then opened
Finally the backup compleetd and if we return the the backup catalog you can see our new backup
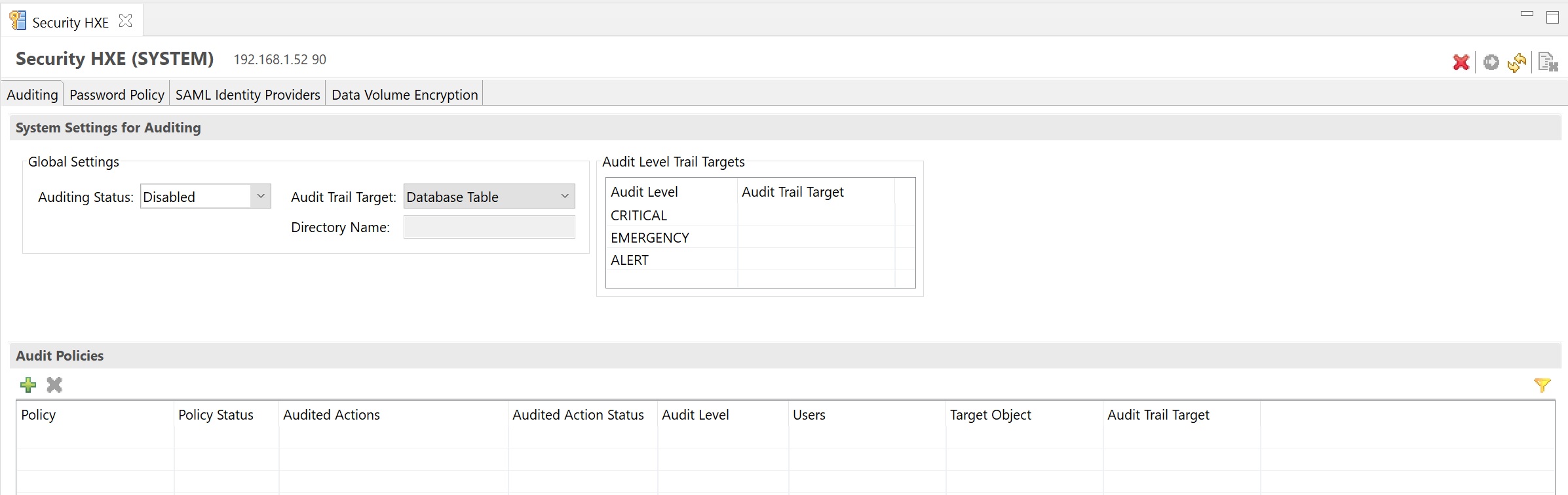
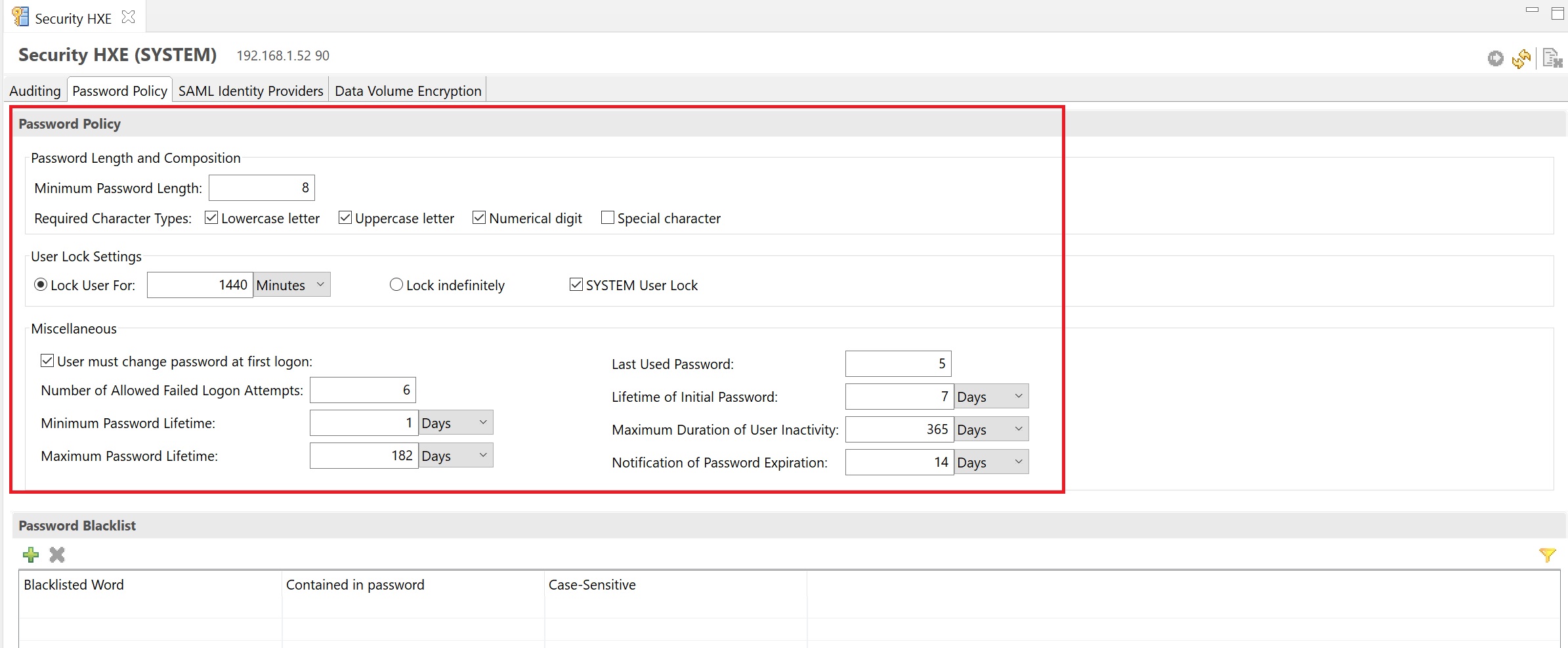
The security screen details audting password policy, etc. The auditing screen allows you to turn on audting for various components by specifying a audit policy.
The password policy allows you to tighten password security, setting the length and strength of the password, also to set the failed login attempts.
An SAML identity provider (IDP) is used by the SAML service provider (SP) to authenticate users signing in by means of a single sign-on (SSO) mechanism.
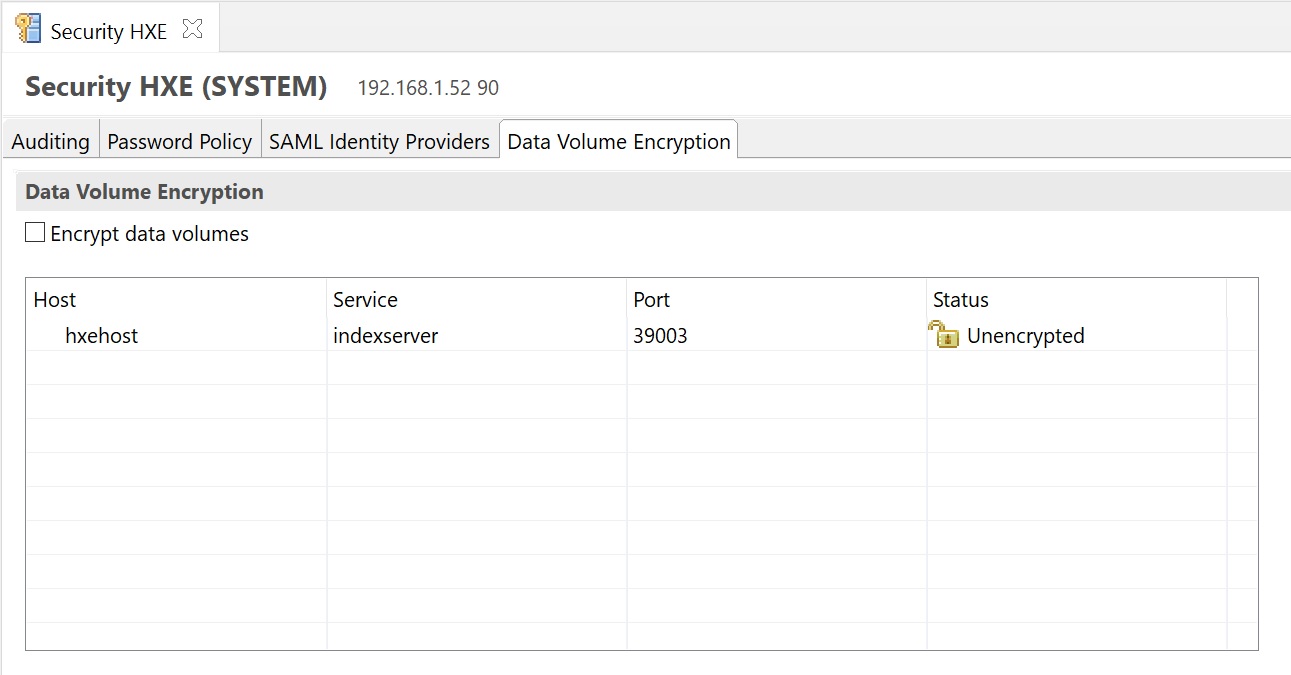
You have the option to encrypt the data volume thus protecting data if for example disk end up on ebay for example
Next we look at the SQL console, here you can enter SQL queries that will be executed against the database
You can use the SAP Hana Modeler if you are a developer, there are a number of developer tools here
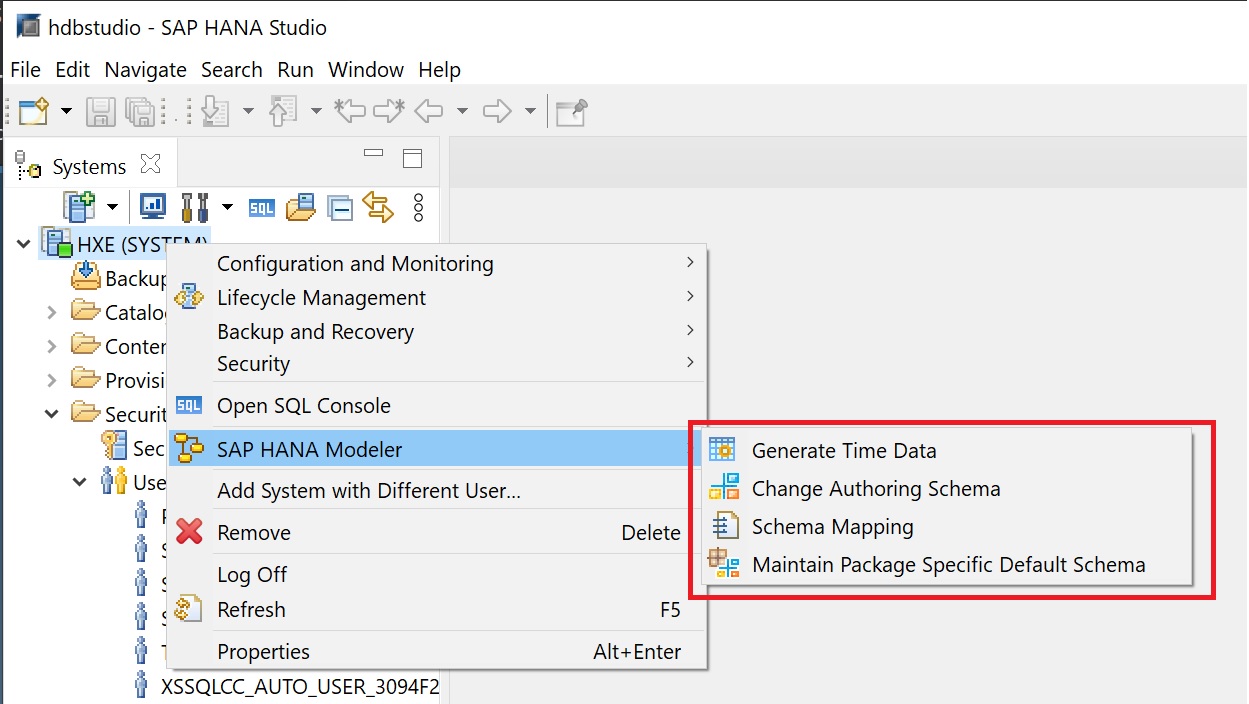
The remaining items allow you to change user, log off, etc.
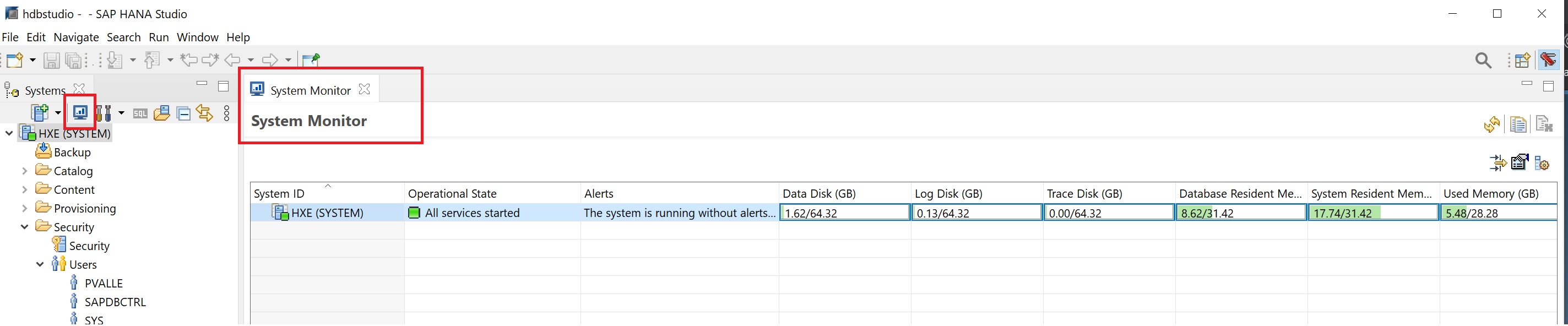
The system monitor icon displays a quick overall of the current system performance (disk sizes and memory allocation)
The Catalog represents SAP HANA’s data dictionary, i. e. all data structures, tables, and data which can be used. All the physical tables and views can be found under the Catalog node.
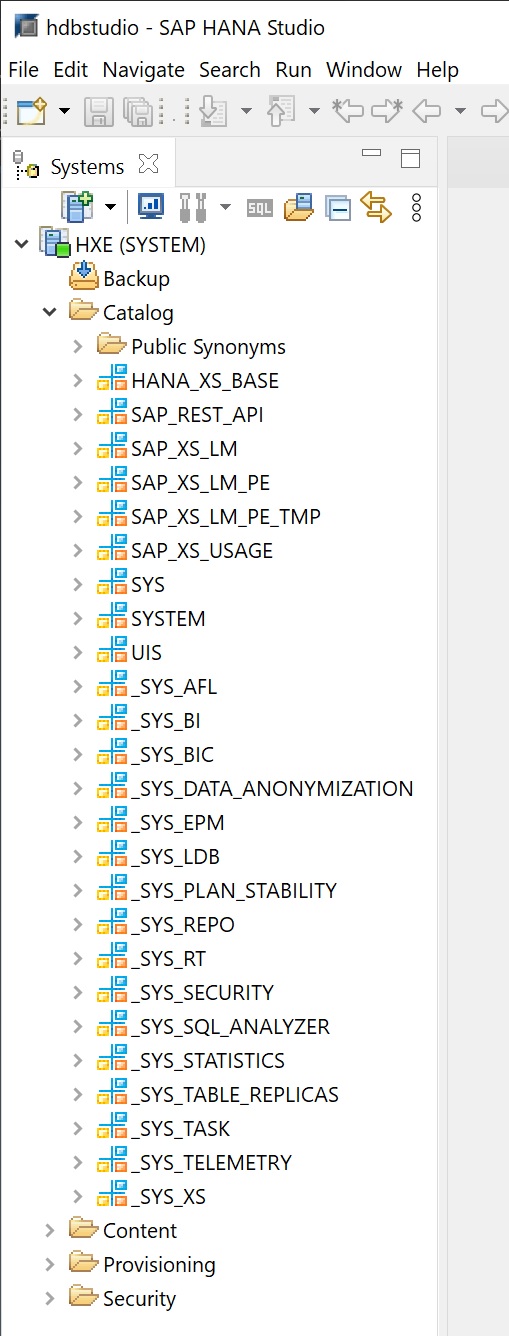
The Content represents the design-time repository which holds all information of data models created with the Modeler. Physically these models are stored in database tables which are also visible under Catalog. The Models are organized in Packages. The Contents node just provides a different view on the same physical data.
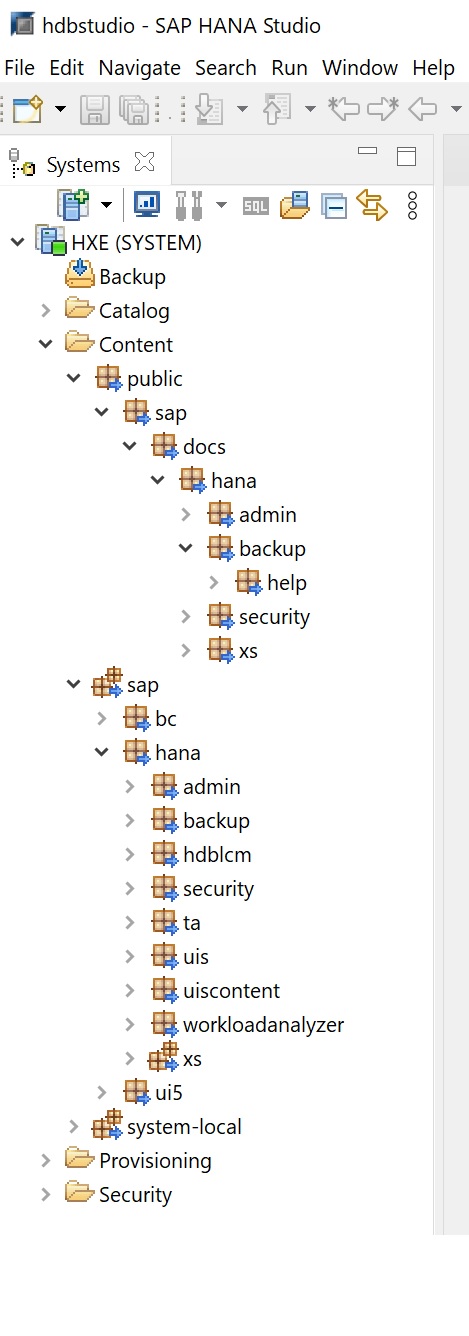
Provisioning is for configuring remote sources and for using SMART DATA ACCESS
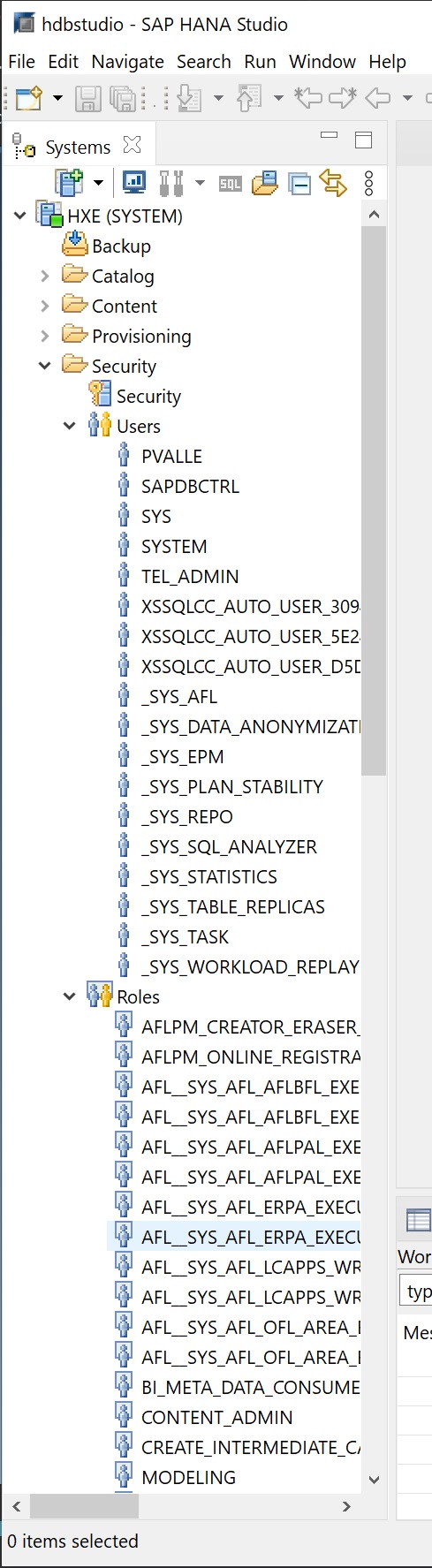
Security is for configuring users and roles
Lastly you can change how Hana studio looks like based on what role you do for example admin or developer.